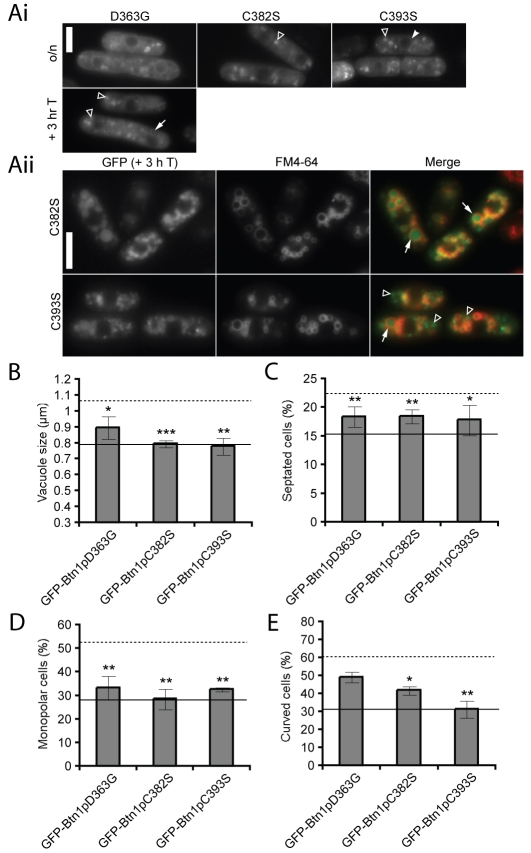
Fig. 5.
Mutations in the C-terminal domain alter the trafficking of Btn1p, but have varying effects on protein function. (A) (i) Localisation of GFP-tagged mutants at steady state (upper panels) and after promoter repression for GFP-Btn1pD363G (lower panel); (ii) GFP-Btn1pC382S and GFP-Btn1pC393S were present inside the vacuole after 3 hours of promoter repression. Cells were co-labelled with FM4-64 to stain the vacuole perimeter. GFP-Btn1pC393S was also visible in pre-vacuolar compartments that were not labelled with FM4-64. Arrow=vacuole, filled arrowhead=ER, unfilled arrowhead=pre-vacuolar compartment. (B-E) Phenotypes of btn1Δ cells expressing the indicated mutant GFP-Btn1p proteins: (B) mean vacuole diameter (μm); (C) mean septation index (% of total cells); (D) mean percentage of monopolar cells (% of total septated cells after 7 hours at 37°C); and (E) mean percentage of curved or bent cells (% of total cells after 4 hours at 37°C). Dotted line=mean value for btn1Δ cells, unbroken line=mean value for btn1Δ cells + GFP-Btn1p. (Data shown is the mean±s.d. of at least three independent experiments; ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05.) Bar, 5 μm.