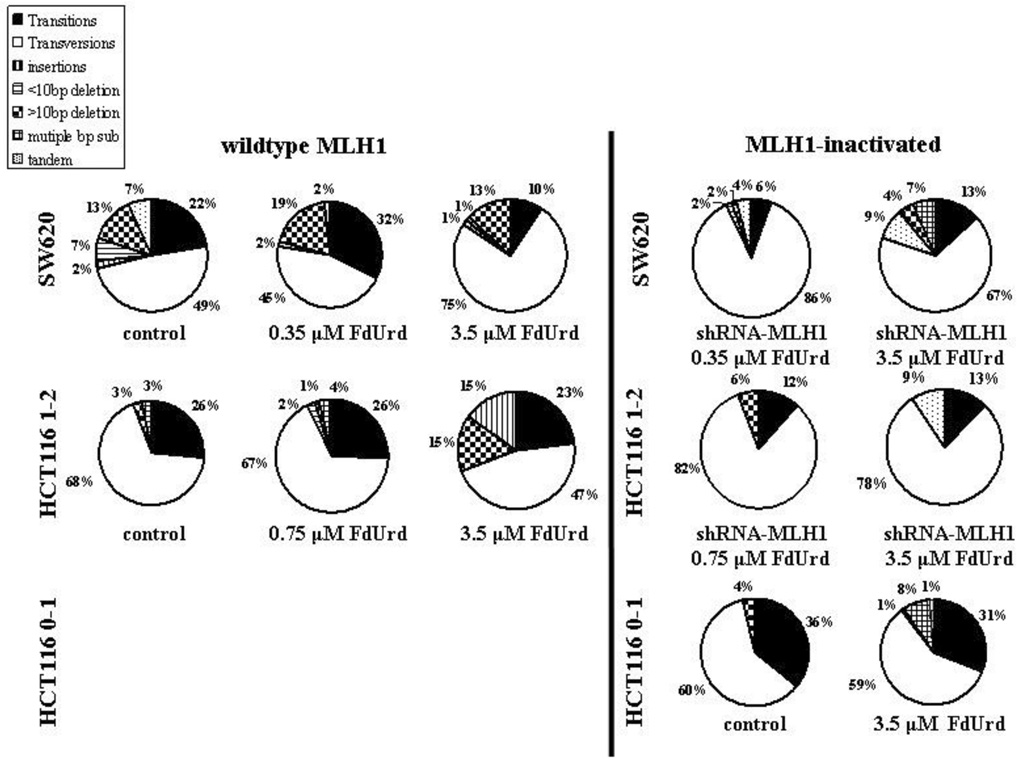
Fig. 2. Type and frequency of mutations in the supF sequence in pSP189 plasmids replicated in HCT116 cells and SW620 cells.
HCT116 0–1 MLH1-inactivated, HCT116 1–2 MLH1-wildtype and HCT116 MLH1-inactivated, and SW620 MLH1-wildtype and SW620 MLH1-inactivated cells were transfected with pSP189 plasmid overnight and exposed to no drug (control), or to 3.5 µM (IC50) (HCT116 0–1 cells) or 0.75 µM (IC50) and 3.5 µM (IC90) (HCT116 1–2 cells), or 0.35 µM (IC50) and 3.5 µM (IC90) (SW620 cells) FdUrd for 24 h. Mutant colonies were picked and grown in LB broth followed by plasmid extraction and DNA sequencing. Mutation frequency was calculated as # white colonies / # (white + blue) colonies. n, the total number of mutant colonies, all of which were submitted for DNA sequencing. At least 26 mutant colonies were counted within each group.