Figure 6. Developmental potential of B-iPS cell lines.
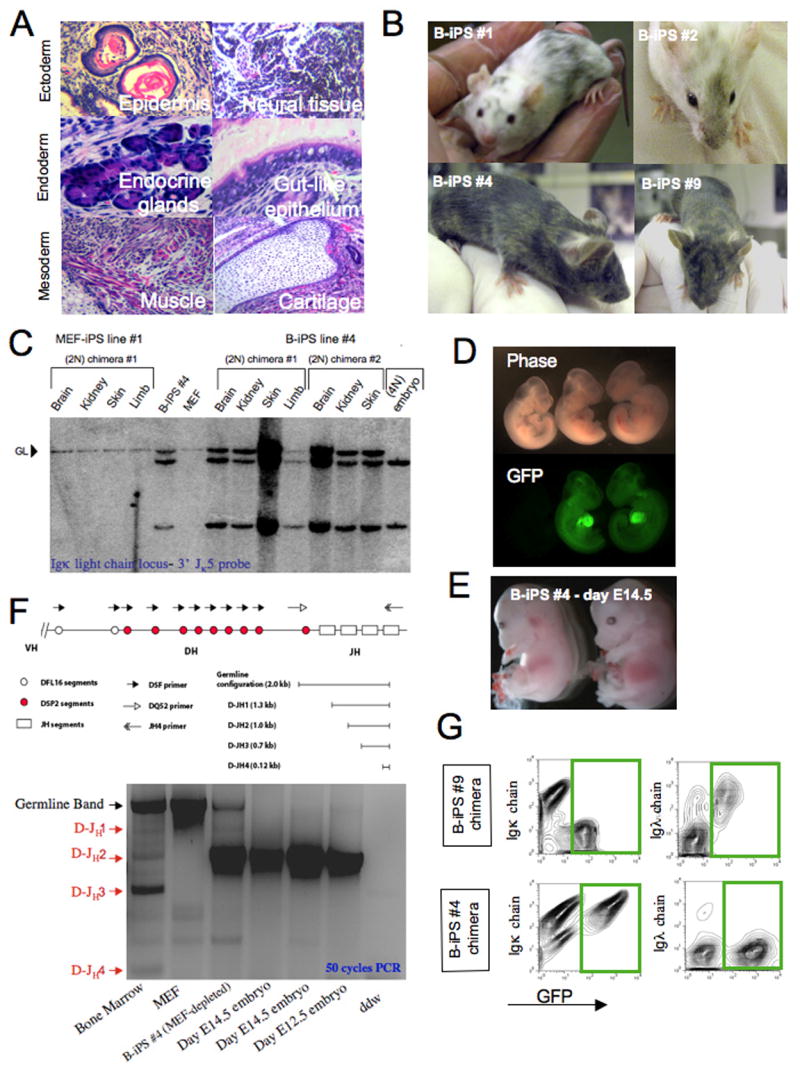
(A) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of a representative teratoma derived from B-iPS line #4. (B) Adult chimeric mice obtained from B-iPS lines in 2N Balb/C or B6D2F1 host blastocysts. (C) Southern blot analysis for detection of IgK light chain rearrangements on BamH1 digested genomic DNA (as detailed in Figure 5A) from different tissues obtained from MEF-iPS #1 derived chimeras (used as negative control) and B-iPS #4 cell line. (D) B-iPS#1 line was transduced with lentiviral ubiquitin-EGFP vector before injection in 2N blastocysts. Germline transmission was achieved from one of the chimeras, as we obtained a number of GFP+ embryos, demonstrating the transmission of constitutively expressed EGFP transgene. (E) “All B-iPS cell embryos” were generated by injection of B-iPS cell into 4N blastocysts. Live E14.5 embryos generated from B-iPS#4 cell lines. (F) Highly sensitive 50 cycle PCR analysis on 4N embryos obtained from B-iPS#4 for detection of loss of the amplicon representing germline line configuration of IgH locus in order to prove that the embryos developed entirely from iPS cells. Equimolar mix of 5′ primers DQ52 (recognizes downstream region that is always excised upon any recombination of the locus) and DSF (degenerate primer recognizing D cassettes) with 3′ JH-4 primer. This PCR could yield 4 rearrangement bands (D-JH1,2,3,4) and a germline 2 Kb band as indicated in the locus scheme. (G) Immunological analysis for detection of Igκ and Igλ surface antigen on peripheral blood B cells of chimeras obtained from constitutively GFP labeled B-iPS #4 and #9 (marked with lentiviral ubiquitin-EGFP vector before injection). Presented panels were gated on CD19+ cells and show Igκ and Igλ expression on iPS derived B cell (GFP+) and host B cells (GFP−). Green rectangles highlight B-iPS derived of GFP+ B cells.
