Figure 1. Concept of the Random Mutation Capture assay.
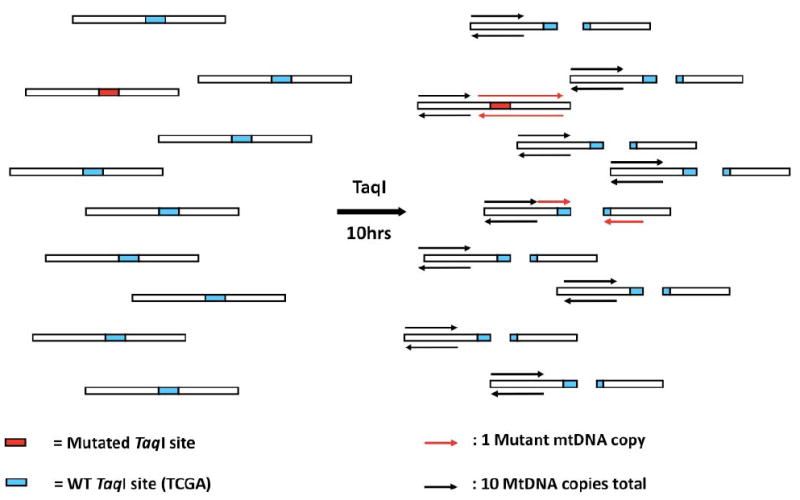
The RMC-assay exploits the ability of TaqI, a restriction enzyme, to discriminate between DNA molecules with either a WT, or a mutant TaqI restriction site. After mtDNA digestion with TaqI, a PCR reaction is attempted across a TaqI restriction site (red arrows). This PCR reaction will amplify only DNA molecules that contain a mutation in the restriction site (red box), that rendered it resistant to cleavage. Amplicons with a WT restriction site (green box) are no longer a template for PCR amplification. These mutant molecules are then quantified by qPCR. A second qPCR reaction, adjacent to the restriction site, quantifes every DNA molecule in a sample. The ratio of mutant molecules to the total number of molecules is a direct measurement of the mutant frequency, which can be used to calculate the mutation frequency per base pair.
