Fig. 4. The effects of 5,14-HEDGE (the synthetic 20-HETE mimetic) and 20-HEDE (the competitive antagonist of vasoconstrictor effects of 20-HETE) on vascular hyporeactivity in isolated thoracic aorta (A, B) and superior mesenteric artery (C, D) 4 h after saline (vehicle) (4 mL/kg, i.p.) or endotoxin (10 mg/kg, i.p.) injection to conscious rats.
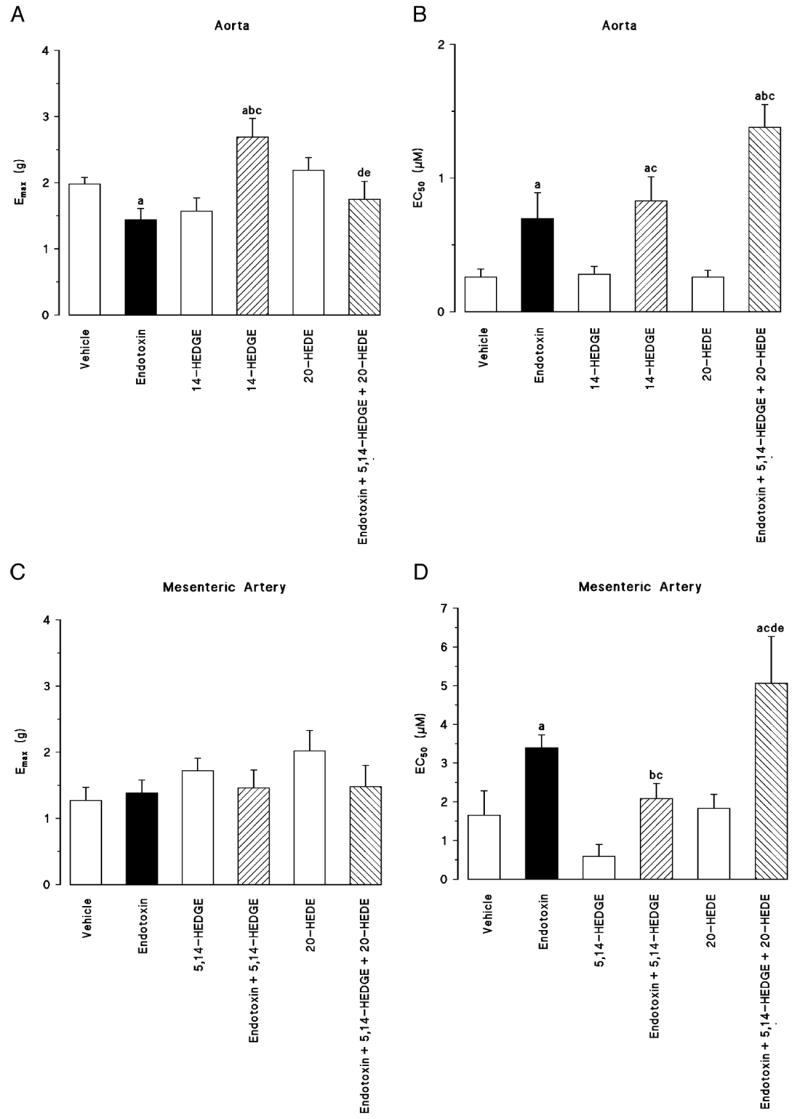
5,14-HEDGE (30 mg/kg, s.c.) or 20-HEDE (30 mg/kg, s.c.) was given 1 h after administration of endotoxin. A and C, Emax. B and D, EC50 values were calculated from cumulative concentration-response curves to norepinephrine (0.001 – 100 μM). Values are expressed as means ± SEM from 5 to 13 rats per treatment group. a indicates a significant difference from the corresponding value seen in rats treated with saline (vehicle) (P < 0.05). b indicates a significant difference from the corresponding value seen in the rats treated with vehicle and endotoxin (P < 0.05). c indicates a significant difference from the corresponding value seen in the rats treated with vehicle and 5,14-HEDGE (P < 0.05). d indicates a significant difference from the corresponding value seen in the rats treated with endotoxin and 5,14-HEDGE (P < 0.05). e indicates a significant difference from the corresponding value seen in the rats treated with vehicle and 20-HEDE (P < 0.05).
