Figure 2. Genetic interactions between Fox factors and ruvb-1 or CeTOR.
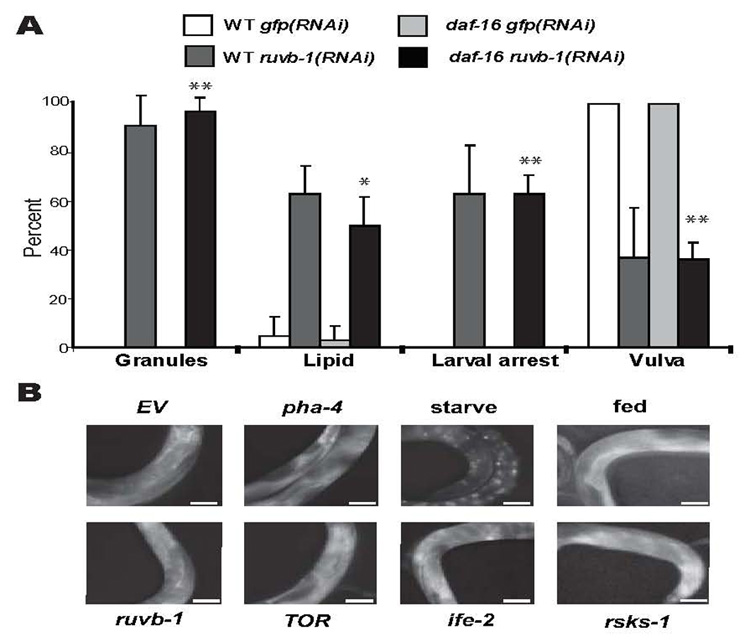
A) ruvb-1 phenotypes do not depend on daf-16/FoxO. RNAi against GFP or ruvb-1 was induced in either wild-type (WT) or daf-16(mu86) hermaphrodites, and their progeny scored by light microscopy for larval arrest, epidermal granules (Granules) or a mature vulva. Lipid accumulation of L3 progeny was determined by Nile Red staining [57] (20°, 3 experiments, n≥24 animals for each condition, error bars denote standard deviation, **p<0.0002, *p=0.0038). B) DAF-16 localization. DAF-16 localization was monitored with daf-16p::daf- 16::GFP [25]. Worms subjected to OP50 (fed), empty vector (EV), ruvb-1(RNAi), pha- 4(RNAi), ife-2(RNAi), rsks-1(RNAi) or let-363(RNAi); daf-15(RNAi) (TOR) show cytoplasmic localization compared to worms starved for 24 hrs, which display nuclear localization (n≥9 worms for each condition, scale bar=50µm).
