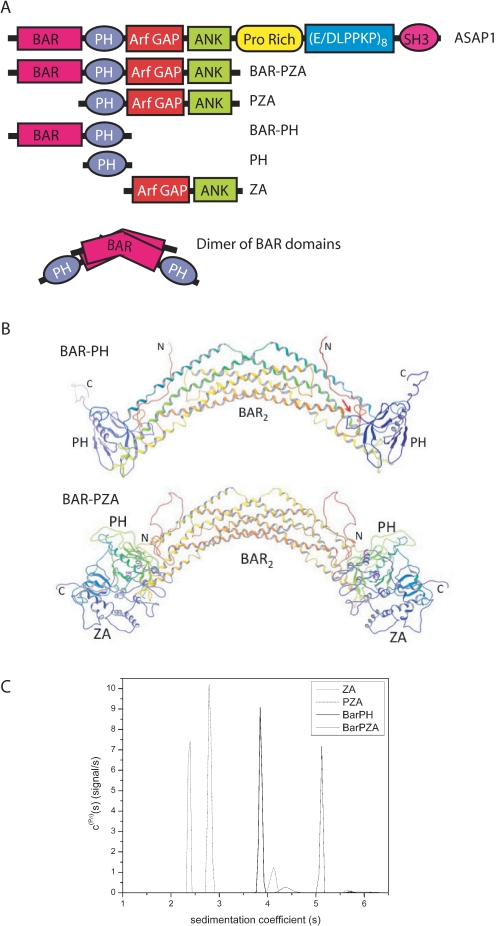
FIGURE 1.
Structure of ASAP1. A, schematic of proteins used in the experiments. The recombinant proteins are schematized with amino acid coordinates indicated. PH, PZA, and ZA have N-terminal His tags. BAR-PZA and BAR-PH have a C-terminal His tag. B, homology models of BAR-PH and BAR-PZA. Shown are backbone ribbon diagrams of the BAR-PH model (top) and BAR-PZA (bottom) shaded from red at the N terminus and violet at the C terminus of each chain of the dimer. The red arrow in the BAR-PH model indicates for the chain on the right the putative region of contact between the BAR N-terminal extension and PH domain loop that forms part of the phosphoinositide binding site. C, analytical ultracentrifugation studies of BAR-PZA, BAR-PH, PZA, and ZA domains. Shown are the sedimentation coefficient distributions c(Pδ)(s) for the indicated protein domains that were obtained from the Bayesian analysis of sedimentation velocity data (42). The integrated weight average sedimentation coefficients, corrected for buffer density and viscosity (s20,w) and the sequence molar mass, were used to calculate the respective protein frictional ratio utilized in hydrodynamic shape modeling (Table 1).