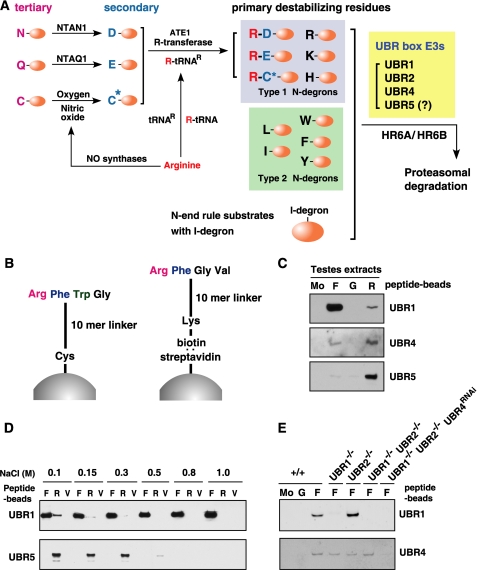
FIGURE 1.
A, the mammalian N-end rule pathway. N-terminal residues are indicated by single-letter abbreviations for amino acids. Yellow ovals denote the rest of a protein substrate. C* denotes oxidized N-terminal Cys, either Cys-sulfinic acid [CysO2(H)] or Cys-sulfonic acid [CysO3(H)]. The Cys oxidation requires nitric oxide and oxygen (O2) or its derivatives. The oxidized Cys is arginylated by ATE1 Arg-tRNA-protein transferase (R-transferase). N-recognins also recognize internal (non-N-terminal) degrons in other substrates of the N-end rule pathway. B, the X-peptide pull-down assay. Left, a 12-mer peptide bearing N-terminal Arg (type 1), Phe (type 2), Trp (type 2), or Gly (stabilizing control) residue was cross-linked through its C-terminal Cys residue to Ultralink Iodoacetyl beads. Right, the otherwise identical 12-mer peptide, bearing C-terminal biotinylated Lys instead of Cys, was conjugated, via biotin, to the streptavidin-Sepharose beads. C, the X-peptide pull-down assay of endogenous UBR proteins using testes extracts. Extracts from mouse testes were mixed with bead-conjugated X-peptides bearing N-terminal Phe (F), Gly (G), or Arg (R). After centrifugation, captured proteins were separated and subjected to anti-UBR immunoblotting. Mo, a pull-down reaction with mock beads. D, the X-peptide pull-down assays using rat testis extracts were performed in the presence of varying concentrations of NaCl. After incubation and washing, bound proteins were eluted by 10 mm Tyr-Ala for Phe-peptide, 10 mm Arg-Ala for Arg-peptide, and 5 mm Tyr-Ala and 5 mm Arg-Ala for Val-peptide. Eluted proteins were subjected to immunoblotting for UBR1 and UBR5. E, cytoplasmic fractions of wild-type (+/+), Ubr1-/-, Ubr2-/-, Ubr1-/-Ubr2-/-, and Ubr1-/-Ubr2-/-Ubr4RNAi MEFs were subjected to X-peptide pull-down assay. Precipitated proteins were separated and analyzed by immunoblotting for UBR1 and UBR4.