Figure 6.
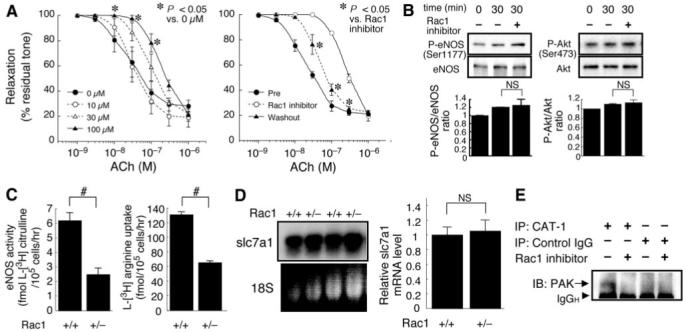
Rac1 promotes endothelial uptake of l-arginine and maintains eNOS function at the posttranslational level. A, Acute inhibition of Rac1 worsens endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation. Left panel, vascular reactivity to ACh was studied using wild-type mice aorta rings (n=3) pretreated with Rac1 inhibitor (0 to 100 μmol/L) for 30 minutes. Right panel, vasorelaxation to ACh was attenuated by Rac1 inhibitor (100 μmol/L) and partially restored following washout for 30 minutes. B, Effect of Rac1 inhibition on the phosphorylation of eNOS (Ser1177) and Akt (Ser473). bEND.3 cells were treated without or with 100 μmol/L Rac1 inhibitor for 30 minutes and harvested for immunoblotting analysis. C, Effect of Rac1 inhibition on endothelial uptake of l-arginine. Rac1+/+ and Rac1+/- MHECs were incubated with 5 μCi/mL (approximately 86.2 nM) l-[3H] arginine for 30 minutes. The eNOS activity and l-arginine uptake was determined as intracellular level of l-[3H] citrulline and l-[3H] arginine, respectively. D, The steady-state mRNA level of slc7a1 gene encoding CAT-1 in Rac1+/+ and Rac1+/- MHECs was determined by Northern blot (left) and real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (right panel, n=6 for each group). E, Effect of Rac1 inhibition on the association of PAK with CAT-1. bEND.3 cells were treated without or with 100 μmol/L Rac1 inhibitor for 30 minutes. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-CAT-1 antibody or IgG (negative control) and subjected to immunoblotting with anti-PAK antibody. *P<0.05; #P<0.01.
