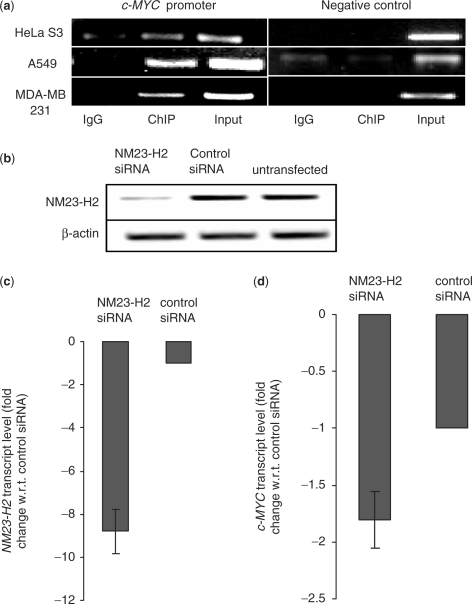
Figure 1.
NM23-H2 binds c-MYC promoter in vivo (a) ChIP assays using antibodies against NM23-H2 in multiple cell lines. Immunoprecipitated DNA samples were PCR amplified to show NM23-H2 occupancy of c-MYC promoter and negative control locus. Primer and locus information are given with ChIP methods; PCR cycles were maintained in the exponential phase of amplification. (b) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of NM23-H2 mRNA expression in A549 cells treated with siRNA duplex against NM23-H2 compared to scrambled (or control) siRNA and untransfected samples. β-actin mRNA levels remain unchanged. (c and d) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis. NM23-H2 (c) and c-MYC (d) transcript levels (fold change is relative to respective transcript levels determined in cells transfected with control siRNA) in A549 cells treated with NM23-H2 siRNA or control siRNA duplex. Experiments were performed in triplicate to analyze standard deviations in all cases.