Figure 1.
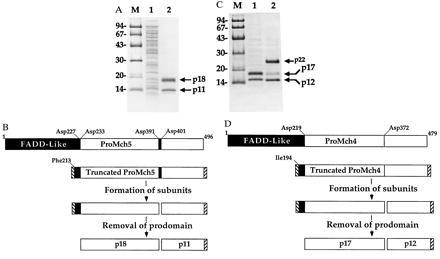
Subunit structure of mature Mch4 and Mch5. Truncated proMch5 (A) and proMch4 (C) lacking most of the FADD-like prodomain (see schematics B and D) were expressed in Escherichia coli, purified to homogeneity, analyzed by SDS/PAGE and Coomassie staining, and then microsequenced. (A) Lane 1, Total bacterial lysate; lane 2, Ni2+-affinity purified mature Mch5 enzyme. The N-terminal amino acid sequence of p11 is LSSPQTRYIPDEADFLLGMA, and the N-terminal amino acid sequences of p18 are SPREQDSESQTLDKVYQMKS and SESQTLD KVYQMKS. (B) A schematic diagram illustrating autoprocessing of proMch5. ProMch5 is autocatalytically processed in two steps to generate the mature p11/p18 enzyme complex. The first step involves processing at Asp-391 and Asp-401, which generates the p11 subunit and nonmature large subunit. This form is enzymatically active and can autoprocess the nonmature large subunit to the mature p18 species by cleavage at Asp-227 and Asp-233 to remove the FADD-like prodomain. (C) Lane 1, Ni2+-affinity purified mature Mch4 obtained after expression of truncated proMch4 (V220-I479); lane 2, Ni2+-affinity purified Mch4 obtained after expression of truncated proMch4 (I194-I479). The N-terminal amino acid sequence of p12 is ALNPEQAPTSLQDSIPAEAD, and the N-terminal amino acid sequence of p17 is VKTFLEALPRA. The N-terminal amino acid sequence of p23 is ASMTGGQQMGRDPIQIVTPP, which contains both the T7 tag (underlined) and the proMch4 sequence. (D) A schematic diagram illustrating autoprocessing of proMch4. Like proMch5, proMch4 undergoes autocatalytic processing in two steps to generate the mature p12/p17 enzyme complex. The first step involves processing at Asp-372, which generates the p12 subunit and nonmature large subunit (in this case p23). The nonmature large subunit is autocatalytically processed to the mature p17 species by cleavage at Asp-219 to remove the FADD-like prodomain. Hatched boxes at the N and C termini of truncated proMch4 or proMch5 represent the T7 and His6 tags, respectively. Lanes M in A and C contain molecular weight markers.
