Figure 2.
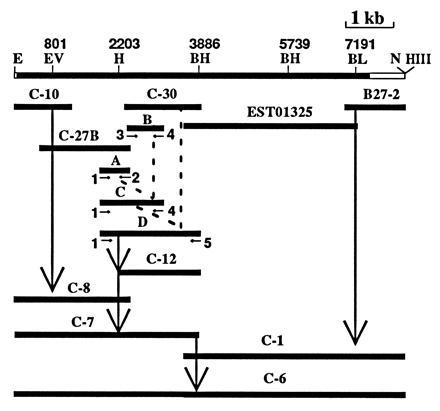
Strategy for engineering a full-length hFAS cDNA clone. The top line shows the location of the restriction sites at the indicated nucleotide number. The cDNA clones C-10 and C-27B were joined together by using EcoRV to generate the N-terminal clone C-8 (nt 1 to 2451). To join the next cDNA clone, C-30, we had to perform recombinant PCR, which generated PCR fragments A, B, C, and D and cDNA clone C-12 as intermediates (see the text for details). The cDNA clone C-7 was obtained by appropriately ligating the HincII fragment from clone C-8 to clone C-12. The cDNA clone C-1, which contained the carboxyl-terminal end of FAS, was generated by joining the EST01325 and B27-2 clones using the common restriction site BclI. To generate the full-length cDNA FAS clone C-6, we had to ligate the BamHI site of C-7 to the BamHI site (nt 5739) of C-1 and then insert the BamHI–BamHI fragment in proper orientation to generate clone C-6. The abbreviations used for the restriction sites are: BH, BamHI; BL, BclI; E, EcoRI; Ev, EcoRV; H, HincII; HIII, HindIII; N, NotI.
