Figure 4.
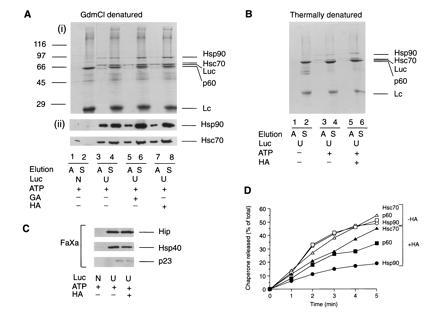
Isolation and characterization of chaperone-bound luciferase from RL. Immunoisolation of chaperone complexes containing unfolded luciferase-myc-His (U) from control lysate and from lysate treated with HA or GA using chemically denatured (A) and thermally denatured (B) luciferase. In A, lanes 1 and 2, native luciferase (N) was added. In B, lanes 1 and 2, thermal denaturation of luciferase was carried out in ATP-depleted lysate. Complexes bound to protein G-Sepharose were eluted with ATP (A) or SDS (S). Eluted fractions were analyzed by SDS/PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining (Ai and B) or immunoblotting with anti-Hsp90 and anti-Hsc70 (Aii). (C) Luciferase complexes were released from Sepharose beads with factor Xa and eluates immunoblotted with antibodies against Hip, Hsp40, and p23. (D) Time course of ATP-dependent elution of chaperones from complexes with luciferase isolated as in A from control lysate (−HA) and HA-treated lysate (+HA). Sepharose beads were incubated for 1 min at 25°C in 200 μl of buffer B with 1 mM ATP/5 mM Mg2+, and the supernatant was removed. This procedure was repeated five times, followed by a final elution with SDS. ATP eluates were analyzed as in A. Proteins were quantified by densitometry and plotted as the amount of total chaperone protein released up to a given time.
