Figure 2.
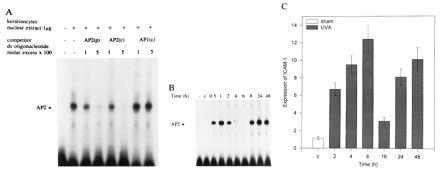
GEMSAs of nuclear extracts from UVA-irradiated (30 J/cm2) cultured human keratinocytes. (A) Binding of nuclear extracts to a double-stranded, radiolabeled oligonucleotide containing an AP-2 consensus sequence deduced from the sequence of the human ICAM-1 promoter (AP-2p) was studied in the presence or absence of unlabeled competitor, a commercially available oligonucleotide containing an AP-2 consensus sequence deduced from the simian virus 40 promoter (AP-2c), or an AP1 consensus oligonucleotide (AP1c) in 100 or 500 M excess. Nuclear extracts were prepared 2 h after irradiation as described. Data represent one of three essentially identical experiments. (B) Time course of the activation of transcription factor AP-2 in keratinocytes after UVA irradiation (30 J/cm2). Nuclear extracts were prepared at different time points as indicated and were analyzed by GEMSA using a radiolabeled oligonucleotide containing an AP-2-binding site. Free radiolabeled oligonucleotides (−) and the sham-irradiated control extract (lane c) were analyzed in lanes 1 and 2, respectively. Data represent one of five essentially identical experiments. (C) Time course of induction of ICAM-1 mRNA expression in cultured human keratinocytes after UVA irradiation (30 J/cm2). Sham-irradiated cells (lane c) served as control. Total RNA was extracted at the indicated times. Expression of ICAM-1 mRNA was analyzed by differential reverse transcriptase-PCR as described. Data are given as mean ± SD of relative ICAM-1 mRNA expression (normalized for glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase expression) of five experiments.
