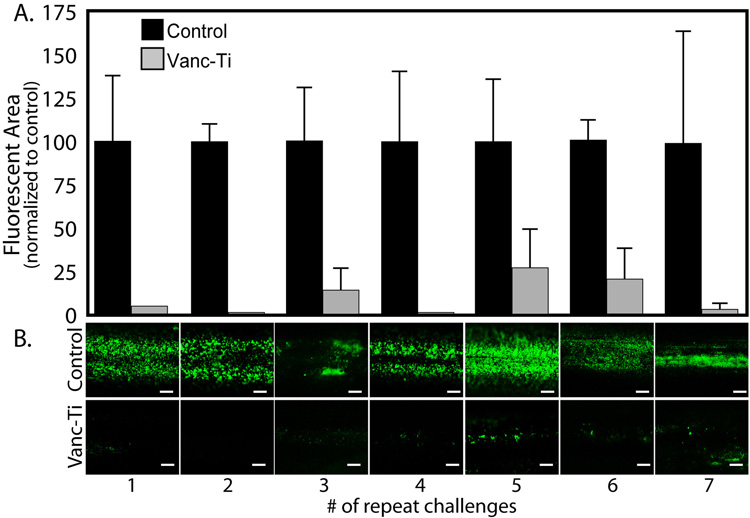
Figure 3. Antibacterial activity of Vanc-Ti rods following multiple challenges.
Control and Vanc-Ti surfaces were incubated with bacteria for 24 h, stripped by detergent lysis, imaged, and re-incubated with bacteria for another 24 h; the cycle was repeated 7 times and bacteria were visualized with the Live/Dead stain. (A) Abundant bacteria (green) colonized the control surfaces. In contrast, the Vanc-Ti showed minimum bacterial staining, indicative of significant inhibition of bacterial colonization after each cycle. Magnification: bar = 200 µm. (B) The fluorescent area of the rods was measured and normalized to the control area for each challenge. Subsequent to the first 3 independent challenges, the surfaces show some variability in their response to further cycles of challenge. Values shown are the average ± S.E. of 3 independent experiments (*Significantly different from control, p < 0.05).