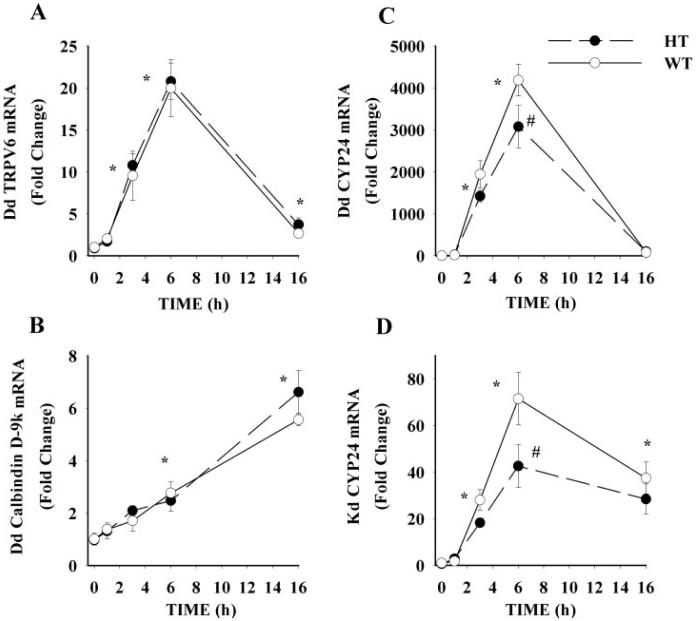
FIG. 2.
Effect of VDR level on the induction of duodenal (Dd) and renal (Kd) gene expression. Ninety-day-old WT and HT mice were injected with a single dose of 1,25(OH)2 D3 (200 ng/100 g BW) or vehicle (control). Animals were killed at indicated time and tissues were harvested for mRNA analysis by real-time PCR. Values for specific targets were normalized to the expression of the constitutively expressed gene GAPDH: A, Dd TRPV6; B, Dd calbindin D9k; C, Dd CYP24; and D, Kd CYP24 mRNA. Gender was balanced across genotype and diet groups and used as a covariate to correct for the higher efficiency of calcium absorption previously seen in female mice (35). Values are expressed as fold change relative to the 0 h time point. Symbols represent the mean ± SEM (n = 6). *, Value different from 0 h for both groups; #, HT value significantly lower than WT value (Fisher's protected LSD, P < 0.05).