Figure 2.
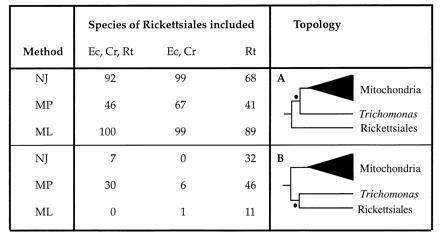
The impact of the sampling of Rickettsiales species on the bootstrap support for two alternative topologies of the cpn60 tree. The dataset excluding the E. histolytica sequence, was used to examine the bootstrap support for two alternative clades each indicated by • on the two trees. (A) The T. vaginalis/mitochondria clade found by neighbor-joining, maximum likelihood and two of the three maximum parsimony trees. (B) The T. vaginalis/Rickettsiales clade displayed by the third maximum parsimony tree (see Materials and Methods). Percentage bootstrap support for each clade is indicated to the left of the trees. Three different combinations of Rickettsiales species were used in the dataset. Species abbreviations are: Ec, Ehrlichia chaffeensis; Cr, C. ruminantium and Rt; R. tsutsugamushi. For each combination of species, bootstrap support for the clade was evaluated using the methods NJ (neighbor-joining distance), MP (maximum parsimony) and ML (protein maximum likelihood) as described in the Materials and Methods.
