Figure 2.
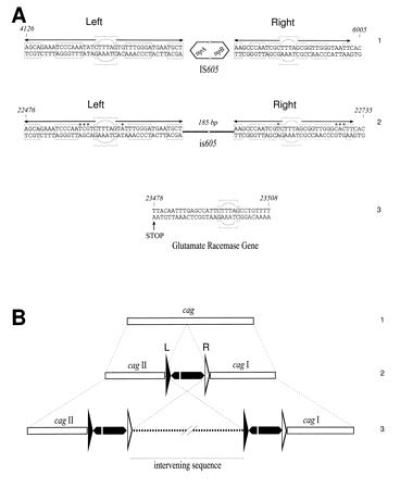
(A) Sequences of the left (L) and right (R) end of IS605 (1) and is605 (2) and the general structure of both elements. The core is formed by a conserved hexanucleotide, inscribed into a circle. The arrows indicate the dyadic structure of the ends. Astericks are nonconserved nucleotides. The sequences included in the boxes are specular. The last 31 bp of glutamate racemase gene, representing the duplicated sequence, are shown (3). The core is marked. Stop is the stop codon of glutamate racemase gene. Coordinates are relative to the cag nucleotide sequence. (B) Summarizes the structure of cag in a collection of strains previously described (4). cag is represented by a horizontal white bar (1). IS605 (2 and 3) and the intervening sequence (3) are indicated as in Fig. 1.
