Figure 2.
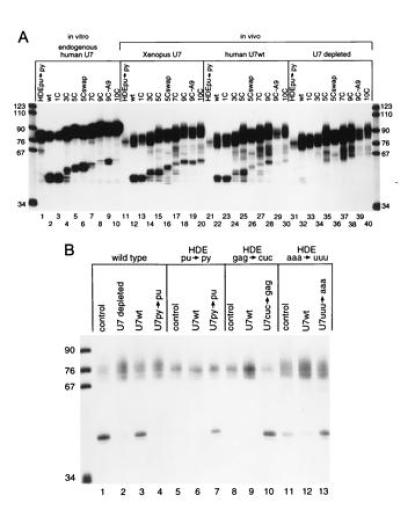
In vitro and oocyte processing of histone pre-mRNA insertion mutants and HDE base substitution mutants. (A) Internally labeled insertion substrates were processed in HeLa cell nuclear extract (lanes 1–10) or injected into the GV of untreated Xenopus oocytes (lanes 11–20), of oocytes where the endogenous Xenopus U7 RNA was degraded and subsequently rescued by injection of in vitro-transcribed human U7 RNA (lanes 21–30), or oocytes where the endogenous Xenopus U7 RNA had been degraded (lanes 31–40). Note that lane 29 was underloaded in this particular experiment. In at least six different experiments, progressive decreases in processing efficiency were observed with longer insertions. (B) Suppression of substitution mutations in the HDE in Xenopus oocytes. Wild-type histone pre-mRNA was injected into untreated oocytes (lane 1), oocytes depleted of U7 RNA (lane 2), depleted oocytes rescued with U7wt RNA (lane 3), or depleted oocytes rescued with U7py→pu (lane 4). In lanes 5–7, the HDEpu-py substrate was injected into untreated oocytes, U7wt rescued oocytes, or U7py→py rescued oocytes. In lanes 8–10, the HDEgag→cuc mutant was injected into untreated, U7wt rescued, or U7cuc→gag rescued oocytes. In lanes 11–13, the HDEaaa→uuu mutant was injected into untreated, U7wt rescued, or U7 uuu→aaa rescued oocytes.
