Figure 1.
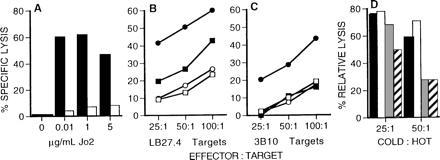
Anti-Fas-resistant cells are refractory to lysis by LCMV-specific CD4+ CTLs. (A) LB27.4 cells (solid bars) or anti-Fas-selected 3B10 cells (open bars) were tested in 51Cr release assays for their ability to be killed by Jo2 mAb. (B and C) LB27.4 (B) and 3B10 cells (C) were tested for their ability to be lysed by splenic effector cells prepared from B6 mice (○, •) or β2m− mice (□, ▪) at 7 or 10 days after i.p. infection with LCMV, respectively. Target cells were either noninfected (○, □) or infected with LCMV 48 hr previously (•, ▪). (D) Unlabeled target inhibition assays were performed using effector cells from LCMV-infected β2m− mice assayed at an effector to 51Cr-labeled target cell ratio of 50:1. The 51Cr-labeled targets (“hot targets”) were LCMV-infected LB27.4 cells. Unlabeled competitor cells (“cold targets”) were added to give cold:hot target ratio of either 25:1 or 50:1. Cold targets were noninfected LB27.4 cells (solid bars), noninfected 3B10 cells (open bars), LCMV-infected LB27.4 cells (shaded bars) and noninfected 3B10 cells (hatched bars). Percent relative lysis was calculated as follows: 100 × (% specific lysis in the presence of cold targets/% specific lysis in the absence of cold targets).
