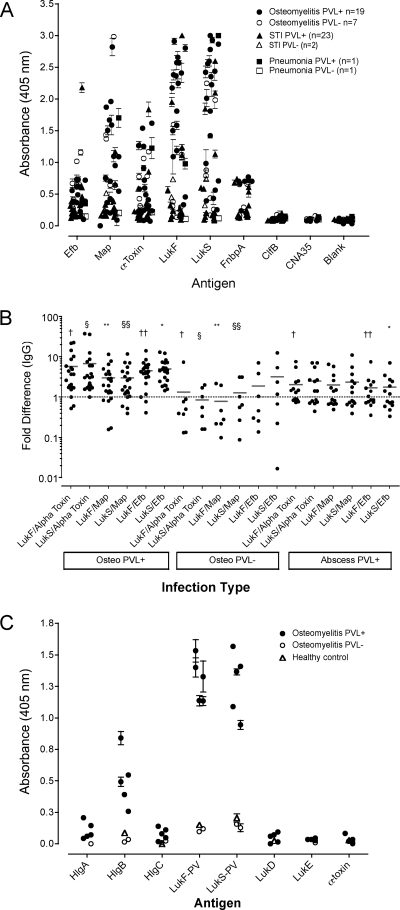
FIG. 1.
Antibody reactivities to S. aureus virulence proteins. ELISA plate wells coated with S. aureus proteins were incubated with a 1:1,000 dilution of patient serum and were then probed with a 1:5,000 dilution of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-IgG antibody. The plates were developed for 30 min in the dark and then read at 405 nm. The data are expressed as the means ± standard errors for triplicate wells per patient. (A) IgG responses to Efb, Map, alpha toxin, LukF-PV, LukS-PV, ClfB, CNA35, and FnbpA in patients with different disease presentations. (B) Log difference in anti-PVL antibody titers. The data are expressed as the log difference between the mean OD readings obtained for individual patients described above. Statistical differences were determined by the unpaired t test with Welch's correction; and differences between groups are indicated by the corresponding symbols: †, P ≤ 0.02; §, P ≤ 0.02; **, P ≤ 0.004; §§, P ≤ 0.04; ††, P ≤ 0.001; *, P ≤ 0.001. (C) Antibody reactivities to S. aureus toxins. ELISA plate wells were coated with 1 μg/well of either HlgA, HlgB, HlgC, LukF-PV, LukS-PV, LukD, LukE, or alpha toxin. The data are expressed as the means ± standard deviations for triplicate wells per patient. PVL+, PVL positive; PVL−, PVL negative; STI, soft tissue infection; Osteo, osteomyelitis.