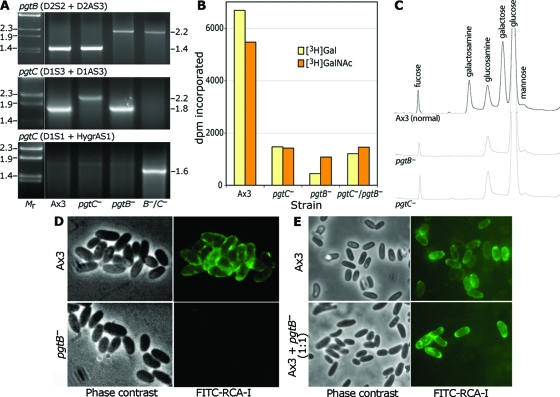
FIG. 3.
Disruption of pgtB or pgtC results in loss of GPS. (A) PCR analysis of disruption strains. gDNA from Ax3 (normal), a pgtB clone, a pgtC clone, and a clone from the double mutant was used as the template for PCRs using the indicated primers specific for the gene indicated. Reactions were resolved on a 1.2% agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide. Size standards in kilobases are to the left, and apparent sizes in kilobases of PCR products are on the right. (B) GPS synthase assay. ISM collected at the time of sporulation was assayed for transfer of 3H from UDP-[3H]Gal or UDP-[3H]GalNAc in a reaction containing GPS acceptor. Values obtained in the absence of acceptor are subtracted for the UDP-[3H]Gal reaction but not the UDP-[3H]GalNAc reaction (see the text). (C) Sugar composition analysis. Equal numbers of parental (Ax3) and mutant spores were subjected to acid hydrolysis (4 M TFA, 4 h, 100°C). Released material was chromatographed on a CarboPac PA-1 HPAEC column with identification by PAD. (D) Lectin probing of parental (Ax3) and mutant (pgtB) spores. Spores were treated with boiling 8 M urea-β-mercaptoethanol and labeled with FITC-RCA-I to detect the GPS. (E) Similar analysis of parental spores and spores formed from a mixture of parental and mutant cells which were codeveloped. The results are representative of at least two independent trials.