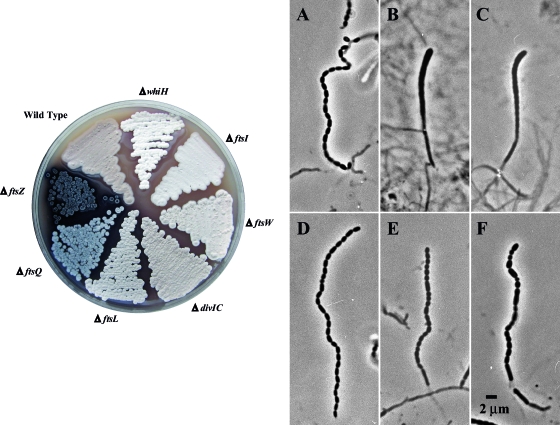
FIG. 2.
Growth phenotypes of mutants and phase-contrast microscopy of wild-type and mutant aerial hyphae. (Left) MS agar medium was used to visualize the gray pigment associated with spore formation within the aerial mycelium (colony surface). Cultures were incubated for 5 days at 30°C. Strains M145 (wild type), HU133 (ΔftsZ), HU151 (ΔftsQ), DU152 (ΔdivIC), DU191 (ΔftsL), JBY5 (ΔftsI), PFB26 (ΔftsW), and J2210 (ΔwhiH, white mutant control) are shown (see Table 1). (Right) Phase-contrast micrographs of coverslip lifts removed after 6 days of growth on R2YE (A to C) or glucose MM (D to F) are shown. Panels A and D show wild-type spore chains (strain M145). Also shown are aerial hyphae of the ftsWSc-null mutant PFB26 (B, R2YE; E, MM) and ftsISc-null mutant JBY5 (C, R2YE; F, MM). The sporulation phenotype is heterogeneous, and only one category of aerial hyphae produced by the division mutants is shown (see text for details).