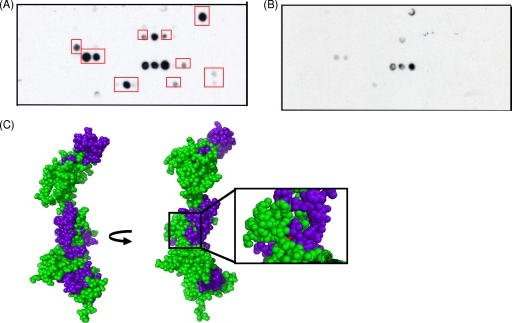
FIG. 2.
Peptides of NusA which bind to DinB encompass the site of the nusA11 temperature-sensitive mutation. (A) One-hour exposure of a cellulose filter peptide array consisting of 12-mer peptides scanning the primary sequence of NusA, with each peptide being offset by two residues from the previous sequence (MIT CCR Core Facility), probed with 150 nM purified recombinant DinB, and developed with an anti-DinB antibody as described previously (34). Recombinant DinB was purified as previously described (3). Red boxes highlight peptides that interacted with DinB and were mapped onto the homology model described below (C). (B) One-hour and 15-min exposures of a control peptide array, which was performed as described above (A) except without a DinB incubation step. (C) Mapping of interacting peptides onto a homology model of NusA. NusA residues are shown in green, interacting peptides are shown in blue, and the temperature-sensitive mutation of the nusA11 allele is shown in red. The NusA homology model, constructed with SWISS-MODEL, is based on the crystal structure of full-length NusA from Thermotoga maritima, with the N terminus of NusA at the top.