FIG. 2.
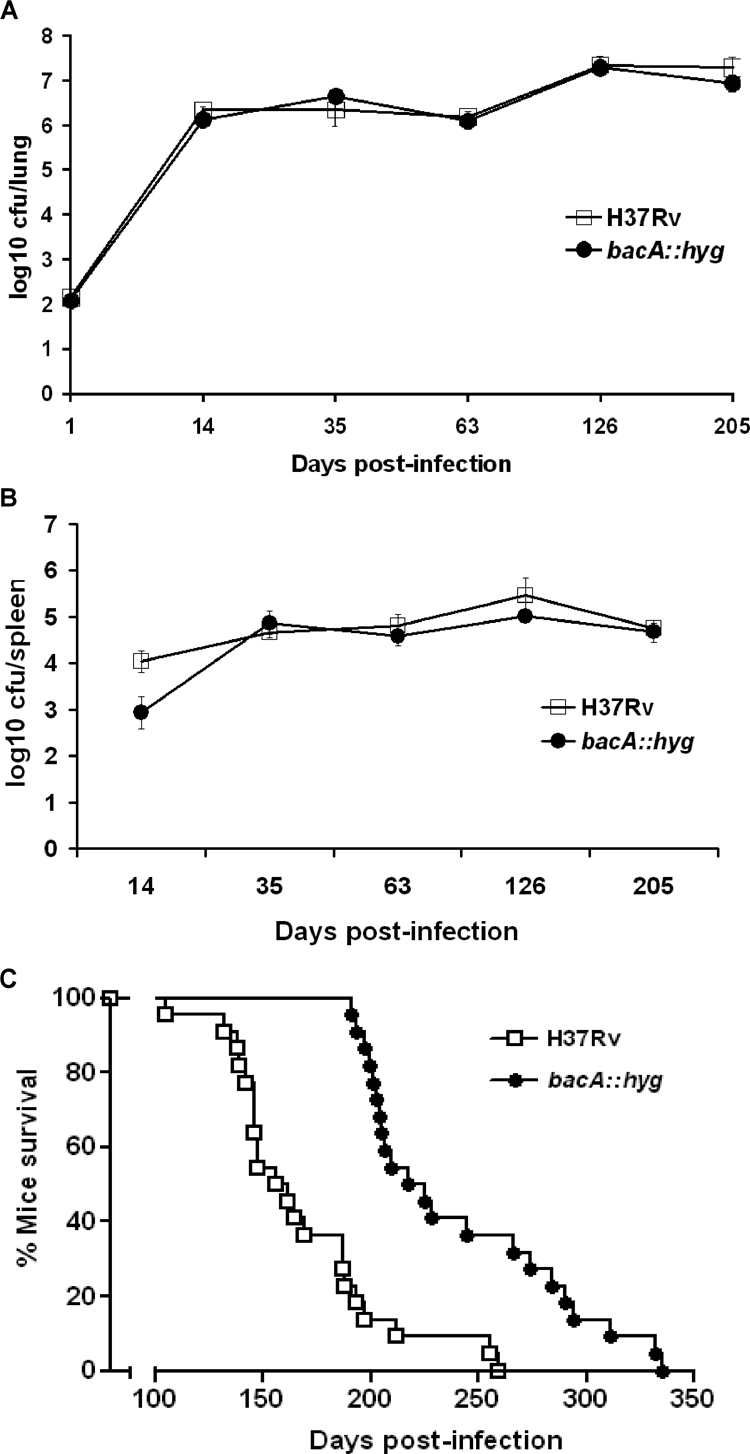
BacA contributes to virulence of M. tuberculosis in mice. B6D2/F1 mice were infected aerogenically with either the bacA::hyg mutant or the parental strain H37Rv. Bacterial numbers were monitored at the indicated times postinfection by harvesting lungs (A) and spleens (B) of infected mice. Results are expressed as averages of log10 CFU/lung along with the standard deviations obtained from replicate platings. (C) Mice were evaluated in a time-to-death experiment with the bacA::hyg mutant and the parental strain H37Rv. Analysis of these data was done using the Kaplan-Meier method, and a log rank test was used to determine statistical significance of observed survival differences (GraphPad Prism v3.0; GraphPad Software, CA).
