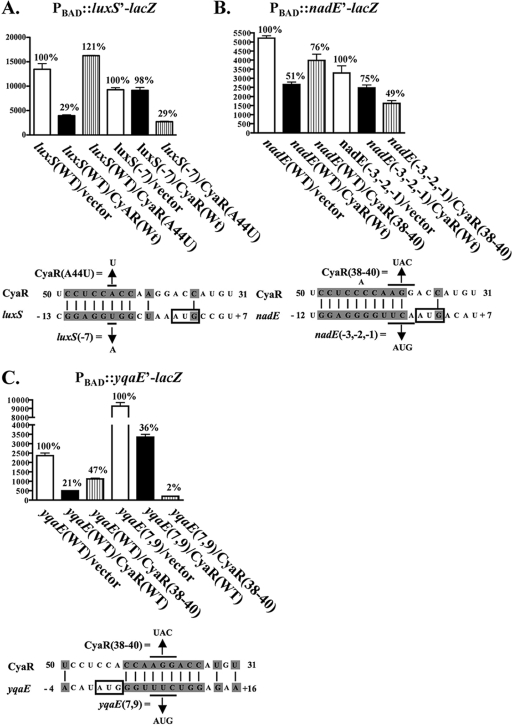
FIG. 5.
β-Galactosidase assays measuring the effect of compensatory mutations in the translation initiation regions of luxS, nadE, and yqaE on restoration of negative regulation by CyaR. Overnight cultures of (A) NRD413 (luxS-lacZ fusion), NRD415 [luxS (T-7A)-lacZ fusion], (B) NRD399 (nadE-lacZ fusion), NRD410 [nadE (T-3A; C-2T; A-1G)-lacZ fusion], (C) NRD400 (yqaE-lacZ fusion), or NRD411 [yqaE (T7A;C9G)-lacZ fusion] harboring pBR-plac (vector), pNRD405 (wild-type cyaR), pNRD407 (cyaR A44T), or pNRD410 (cyaR G38C G39A A40T [CyaR(38-40)]) were diluted 200-fold in fresh LB liquid medium containing IPTG (100 μΜ), ampicillin (100 mg liter−1), and arabinose (0.01%). After the strains were incubated at 37°C for 6 h, the OD600 of each culture was determined, and β-galactosidase assays were performed as described in Materials and Methods. The variant of the lacZ translational fusion examined and the variant of CyaR expressed, if any (bases changed in the lacZ translational fusion or in cyaR are indicated), are indicated on the x axis. The percentage of β-galactosidase activity relative to the activity of the strain harboring the empty vector is indicated above each bar. Below the graphs showing the results of the β-galactosidase assays are diagrams showing the predicted pairing between CyaR and the mRNA encoding luxS (A), nadE (B), or yqaE (C) and the base substitutions in cyaR and the compensatory base changes made in the mRNAs encoding the genes. The start codon of each gene is indicated by a box. The results are averages of two independent experiments. Wt and WT, wild type.