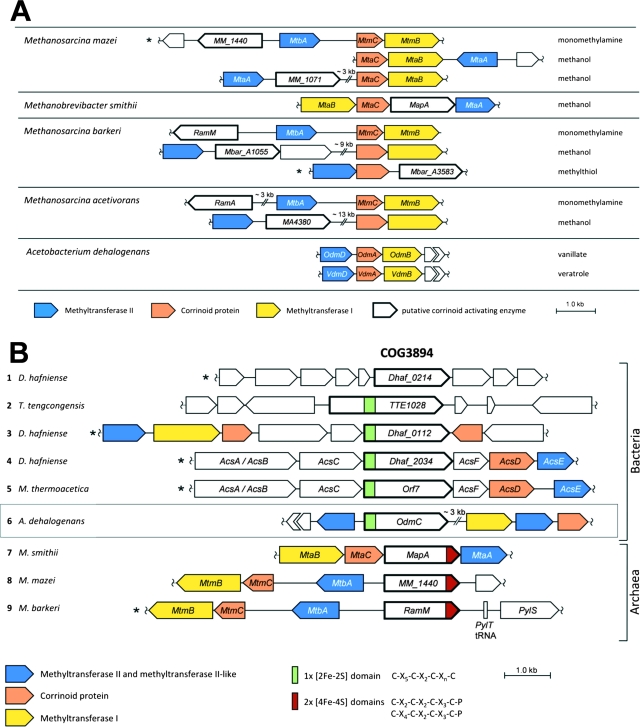
FIG. 3.
Analysis of the O-demethylase genes. (A) Comparison of the MTII/CP/MTI gene clusters of the vanillate- and veratrol-O-demethylases of Acetobacterium dehalogenans with those encoding some methanogenic MT systems of Methanosarcina barkeri, Methanosarcina acetivorans, Methanosarcina mazei, and Methanobrevibacter smithii. For further explanation, see the text. (B) Comparison of the genetic context of the AE gene with gene clusters with orthologs implied in activation of CPs of anaerobic MTs or CODH/ACS. Nine selected bacterial (1 to 6) and archaeal (7 to 9) gene clusters are shown with the COG3894 genes for the putative protein of Desulfitobacterium hafniense DCB-2 (1), the putative Fe/S protein of Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis (2), trimethylamine MT of D. hafniense DCB-2 (3), CODH/ACS of D. hafniense DCB-2 (4), CODH/ACS of Moorella thermoacetica (32) (5), AE (OdmC) of Acetobacterium dehalogenans (6), MapA in the methanol:coenzyme M (CoM) MT of Methanobrevibacter smithii (7), monomethylamine:CoM MT of Methanosarcina mazei (8), and RamM in the monomethylamine:CoM MT of Methanosarcina barkeri (9). Map, MT-activating protein; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine binding domain. The organisms whose gene clusters have been oriented in reverse direction in comparison to the orientation in the annotated genome are marked with an asterisk.