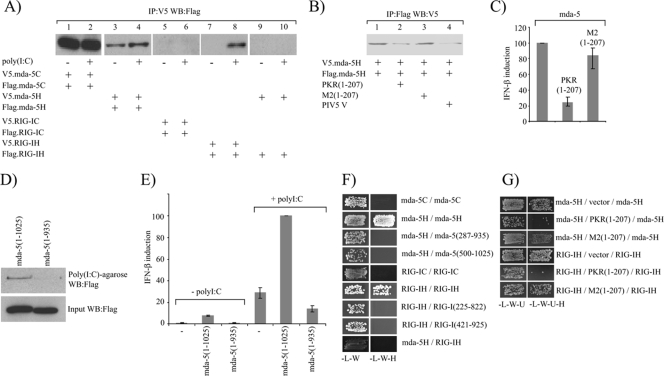
FIG. 5.
The helicase domains of mda-5 and RIG-I contain a dsRNA-dependent oligomerization domain. (A). 293 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing V5- and Flag-tagged forms of the mda-5C domains (lanes 1 and 2), V5- and Flag-tagged forms of the mda-5H domain (lanes 3 and 4), V5- and Flag-tagged forms of the RIG-IC domains (lanes 5 and 6), V5- and Flag-tagged forms of the RIG-IH domain (lanes 7 and 8), or V5-tagged mda-5H and Flag-tagged RIG-IH (lanes 9 and 10). Where indicated (+), one of each pair was transfected the following day with poly(I-C) for 8 h prior to harvesting. Cell extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with an antibody against the V5 tag, and then the presence of the Flag-tagged protein in the immunoprecipitate was analyzed by Western blotting (WB). Expression of all tagged proteins was confirmed by Western blotting on the cell extracts (data not shown). The experiment was performed three times, images were scanned using a Molecular Dynamics Storm 840 PhosphorImager and quantitated using ImageQuant software, and the increase in the amount of Flag-tagged mda-5H in lane 4 compared to lane 3 was determined to be statistically significant by Student's t test with a P value of <0.05. (B). Extracts were prepared from 293 cells transfected with plasmids expressing either Flag-mda-5H, V5-mda-5H, the dsRNA-binding domains of PKR [PKR(1-207)], a mutant form of PKR that is unable to bind dsRNA [M2(1-207)], or the PIV5-V protein. In vitro oligomerization assays were performed by mixing together 50 μl extract from cells expressing Flag-mda-5H with 50 μl extract from cells expressing V5-mda-5H in the presence of 300 μl buffer (lane 1), 300 μl extract from cells expressing PKR(1-207) (lane 2), 300 μl extract from cells expressing M2(1-207) (lane 3), or 300 μl extract from cells expressing PIV5-V (lane 4). Following incubation for 1 h at 4°C to allow complexes to form, immunoprecipitation assays were carried out using an antibody against the Flag tag and the presence of the V5-tagged protein in the immunoprecipitate was determined by Western blotting. The experiment was performed three times, and the reduction in V5-tagged protein in the immunoprecipitate in the presence of PKR(1-207) and PIV5-V was determined to be statistically significant according to Student's t test with P values of <0.01 and <0.05, respectively. (C) 293 cells were transfected with pIFΔ(−116)lucter, pJatlacZ, 80 ng of a plasmid expressing mda-5 and 160 ng of either the empty vector pEFpl2, a plasmid expressing the dsRNA-binding domains of PKR [PKR(1-207)], or a plasmid expressing a mutant form of PKR that is unable to bind dsRNA [M2(1-207)]. Luciferase and β-galactosidase assays were carried out 48 h after transfection, and relative expression levels were calculated. The results shown represent the average from three independent experiments, with the highest and lowest values shown as error bars. A reference value of 100% has been assigned to the level of induction seen in the presence of full-length mda-5. (D) Extracts from 293 cells expressing Flag-tagged full-length mda-5(1-1025) or Flag-tagged mda-5(1-935) were incubated with poly(I-C)-agarose beads for 1 h at 4°C. After washing the beads, bound proteins were analyzed by Western blotting for the Flag tag (upper panel). Expression of both proteins was confirmed by Western blotting of the cell extracts (lower panel). (E) Vero cells were transfected with pIFΔ(−116)lucter, pJatlacZ, and either the empty vector pEFpl2, a plasmid expressing full-length mda-5, or a plasmid expressing mda-5(1-935). After 24 h, the cells were either left untreated or were transfected with poly(I-C). Luciferase and β-galactosidase assays were carried out 48 h after transfection, and relative expression levels were calculated. The results shown represent the average from three independent experiments, with the highest and lowest values shown as error bars. A reference value of 100% has been assigned to the level of induction seen in the presence of full-length mda-5 and poly(I-C). (F) Interactions between the CARD and helicase domains of mda-5 and RIG-I were assessed in the yeast two-hybrid assay. Yeast cells were transformed with plasmids expressing the indicated fragments of mda-5 and RIG-I as GAL4 DBD fusions (given first) and GAL4 AD fusions (given second). Positive transformants were selected on SD −L −W, and growth on this medium demonstrates that the yeast cells have been transformed by both plasmids. They were then streaked onto SD −L −W −H plus 5 mM 3-AT, and growth on this medium demonstrates an interaction between the two proteins. (G) The dependence of the helicase domain interactions on the presence of yeast dsRNA was assessed. Yeast cells were transformed with a plasmid expressing a GAL4 DBD fusion protein (given first), a plasmid expressing a GAL4 AD fusion protein (given third), and either the empty vector pHON7, pHON7 expressing the dsRNA-binding domains of PKR [PKR(1-207)], or pHON7 expressing a mutant form of PKR that is unable to bind dsRNA [M2(1-207)] (given second). Positive transformants were selected on SD −L −W −U, and growth on this medium indicates that the yeast cells have been transformed by all three plasmids. They were then streaked onto SD −L −W −U −H plus 5 mM 3-AT, and growth on this medium demonstrates an interaction between the GAL4 DBD fusion protein and the GAL4 AD fusion protein.