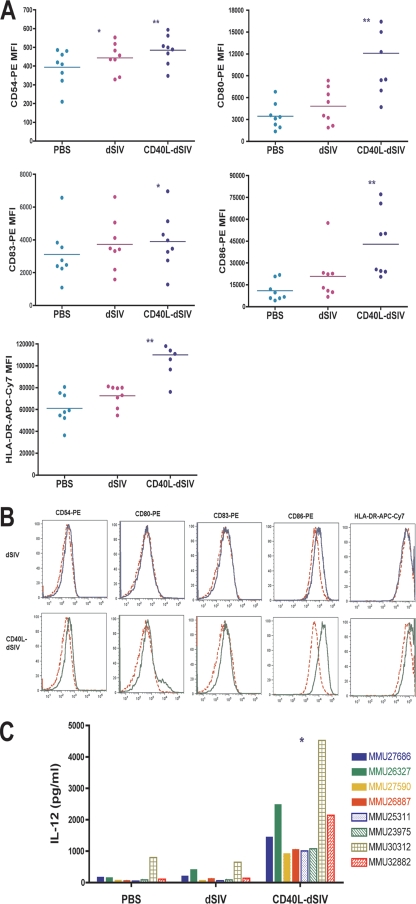
FIG. 4.
Transduction of DCs by CD40L-dSIV results in greater DC activation. (A) The expression level of surface molecules on virus particle-transduced DCs was examined 2 days after transduction by flow cytometry with cells derived from eight different animal donors. Transduction with CD40L-dSIVs resulted in activated DCs and significantly increased levels of CD54, CD80, CD86, and HLA-DR expression compared to results for the PBS and dSIV-transduced groups. The expression of CD83 on CD40L-dSIV-transduced DCs is significantly increased compared to results for the PBS group, but there is no difference from the dSIV-transduced group. DCs were gated using forward scatter, side scatter, and CD11c. Results show the mean florescent intensity of CD11c+ cells in different channels. The expression levels of surface molecules on transduced DCs for all the experimental animals are presented as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). Data were analyzed with the paired t test: *, P < 0.04 compared with results for the PBS group; **, P < 0.004 compared individually with results for the dSIV and PBS groups (n = 8). Bars represent mean values. (B) Flow cytometric data from cells derived from a representative animal donor (out of eight). PBS (red dashed line), dSIV (blue solid line), and CD40L-dSIV (green solid line) groups are shown. (C) IL-12 production is significantly enhanced in CD40L-dSIV-transduced DCs. DC culture supernatants were collected 2 days after transduction with dSIVs and evaluated for the IL-12 p40 concentration using ELISA. The IL-12 concentration in the culture supernatants of CD40L-dSIV-transduced DCs is as much as 6 to 18 times more than that measured in the culture supernatant of dSIV- and PBS-transduced DCs. The assay was done with eight different animals, and a two-tail paired t test was used for data analysis: *, P < 0.003 compared to results for PBS and dSIV individually.