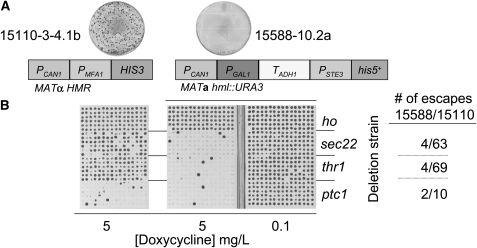
Figure 6.—
Reducing MRA escape increases sensitivity of gene–gene interaction analysis. (A) MRA escape is depicted for 15110-3-4.1b and 15588-10.2a by the petri dishes (MRA factors for each strain indicated below). (B) The frequency of false-negative results for known lethal interactions is reduced 80–95% in association with reduction of MRA escape. A chromosomal Tet-RNR1∷ClonNat “query” allele was introduced into 15110-3-4.1b and 15588-10.2a. Haploid double-mutant strains, involving hoΔ0∷KanMX (used as a “wild-type” negative control), sec22Δ0∷KanMX, thr1Δ0∷KanMX, or ptc1Δ0∷KanMX alleles were obtained in 96-replicate by the SGA method. Interactions were assessed by conditionally expressing RNR1 on C media + 0.1 μg/ml or 5 μg/ml doxycycline. False-negative interactions were reduced by 80% (ptc1) to 95% (thr1) for 15588-10.2a compared to 15110-3-4.1b.