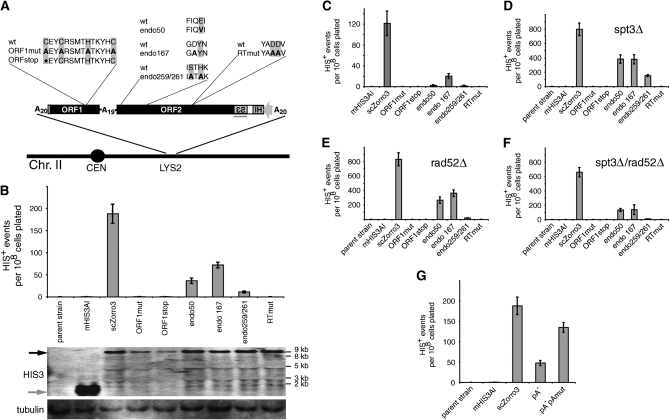
Figure 2.—
Requirements for scZorro3 retrotransposition in S. cerevisiae. (A) Amino acid comparison of wild-type and mutant scZorro3's used in this study. These sequences were integrated into the LYS2 locus in B, D, E, F, and G. Thin bars represent the high and low range of experiments. (B) Retrotransposition of integrated Zorro3/marker variants in wt (GRF167) cells. Total RNA blot for the corresponding strains shown in the bottom sections. Solid and shaded arrows indicate expected positions of scZorro3 transcripts and mHIS3AI-only transcripts, respectively. The location of the HIS3 probe is shown as a shaded line in A. Tubulin, loading control. (C) 2μ plasmid-based retrotransposition in wt (GRF167) cells. (D–F) Retrotransposition of integrated Zorro3/marker variants in spt3Δ cells, rad52Δ cells, and spt3Δrad52Δ cells, respectively. (G) Effect of scZorro3 poly(A) tract deletion/mutation in wt cells. See supplemental Figure S3 for frequencies of individual experiments.