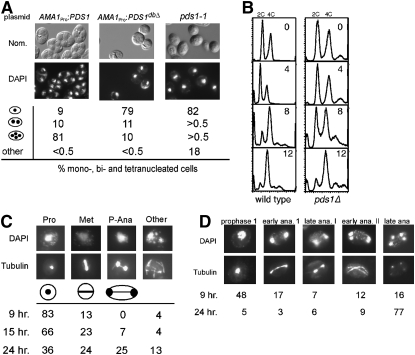
Figure 1.—
Pds1p regulates meiotic progression. (A) Pds1p destruction is required for meiotic progression. Wild-type culture (RSY335) harboring either wild-type or nondegradable Pds1p mutant (PDS1dbΔ) plasmids (pMSC13 and pMSC14, respectively) under the control of the meiosis-specific AMA1 promoter and pds1-1 cells (KCY348) were induced to enter meiosis at 23°. After 24 hr, nuclear divisions and spore formation were analyzed by DAPI staining (bottom) or Nomarski imaging (top), respectively. Percentages of the culture containing one, two or three-plus-four, or fragmented nuclei are indicated. Fragmented nuclei were scored as described in materials and methods. (B) Pds1p is not required for premeiotic S phase. Wild-type (RSY335) and pds1Δ (RSY787) diploid strains were induced to enter meiosis at 23° and samples were taken at the times indicated (in hours) and then analyzed by FACS. Peaks of 2C (unreplicated) and 4C (replicated) are indicated. (C and D) Terminal meiotic arrest phenotypes of pds1Δ mutants. Wild-type (RSY335, D) and pds1Δ (RSY787, C) diploid strains were induced to enter meiosis at 23° and samples were taken at the times indicated. Nuclear and spindle morphologies were determined by DAPI staining (top) and indirect immunofluorescence of tubulin (bottom). Cells were scored as described in materials and methods. For all morphology quantitations presented, the standard deviations were ≤6% for all values. Magnification is ×1000. (D) All strains used (except KCY348, which is derived from the A364A background) are isogenic to RSY335, our standard SK1/303 wild type.