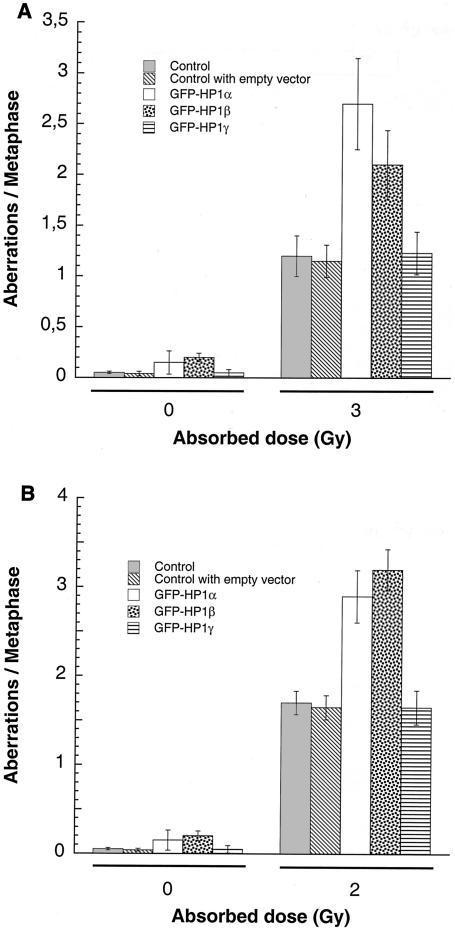
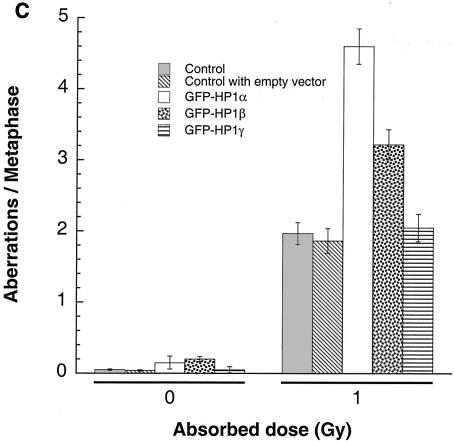
FIG. 9.
G1, S, and G2 chromosomal aberrations after IR treatment. (A) Cells in plateau phase were irradiated with 3 Gy, incubated for 24 h postirradiation, and then subcultured, and metaphases were collected. G1-type aberrations were examined at metaphase. Categories of asymmetric chromosomal aberrations scored included dicentrics, centric rings, interstitial deletions and acentric rings, and terminal deletions. The frequency of chromosomal aberrations was higher in EC-293 cells overexpressing wild-type GFP-HP1Hsα and GFP-HP1Hsβ but not in cells overexpressing GFP-HP1Hsγ. (B) Cells in exponential phase were irradiated with 2 Gy. Metaphases were harvested 6 h following irradiation and examined for chromosomal aberrations. The frequencies of chromatid and chromosomal aberrations were higher in EC-293 cells overexpressing wild-type GFP-HP1Hsα or GFP-HP1Hsβ than in those expressing GFP-HP1Hsγ. (C) Cells in exponential phase were irradiated with 1 Gy. Metaphases were harvested 1 h following irradiation and examined for chromosomal aberrations. The frequency of chromatid aberrations was higher in EC-293 cells overexpressing wild-type GFP-HP1Hsα or GFP-HP1Hsβ but not in those expressing GFP-HP1Hsγ. Note that cells overexpressing GFP-HP1Hsα or GFP-HP1Hsβ have higher frequencies of chromosomal aberrations than those of the parental control cells in all phases of the cell cycle, suggesting a global defective DNA repair.