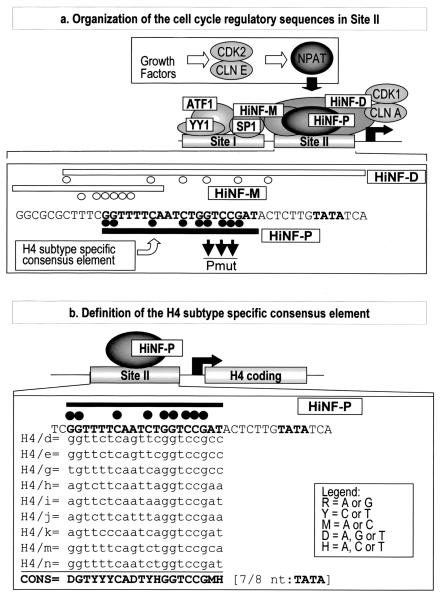
FIG. 1.
Site II-dependent cell cycle control of histone H4 gene transcription. (a) The diagram of the H4 promoter (middle) shows two genomic sites of protein-DNA interactions (site I and site II) and the cognate factors (36). The three site II proteins, HiNF-P, -D, and -M, recognize overlapping motifs (lower portion). Minimal element boundaries defined by DNase I footprinting and deletion analyses are indicated by the open or closed lines, and protein-DNA contacts established by dimethyl sulfate fingerprinting are depicted by closed or open circles. The growth factor-dependent CDK2/CLNE/NPAT pathway that functions to activate histone H4 gene transcription is also indicated (top). (b) The histone H4 subtype-specific consensus element is located upstream from the TATA box within site II and was defined based on nine representative functionally expressed H4 genes.