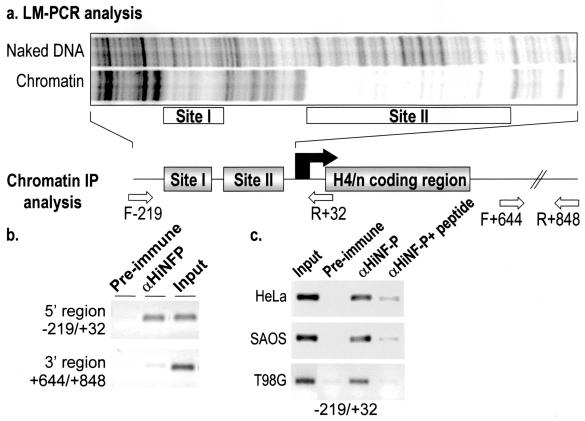
FIG. 4.
Genomic occupancy of HiNF-P at the site II cell cycle element. (a) Genomic occupancy of the HiNF-P binding element within Site II was established in proliferating HL-60 cells by LM-PCR-assisted DNase I footprinting with primers that amplify the proximal promoter of the H4/n gene. The locations and sizes of site I and II are similar to those previously established in HeLa cells by genomic Southern blotting (30). IP, immunoprecipitation. (b) The interaction of HiNF-P with the H4/n promoter in vivo was determined by ChIP with an HiNF-P antibody (αHiNFP). Genomic segments derived from the H4 locus in chromatin precipitates from HL-60 cells were detected by using PCR primers spanning 5′ (−219 to +32) or 3′ (+644 to +848) regions. Amplified products from the 5′ region are observed in input chromatin and in the precipitate with the HiNF-P antibody but not in precipitates obtained with preimmune serum. The 3′ primer pair amplifies DNA only from input samples and serves as a negative control. (c) ChIP was performed with preimmune serum (IgG), HiNF-P antiserum (αHiNF-P), and HiNF-P antiserum preincubated with the antigenic peptide (αHiNF-P + peptide) by using chromatin (input) isolated from different cell types (HeLa, Saos-2, and T98G). The presence of the H4 promoter in chromatin immunoprecipitates was detected with the F−219-R+32 PCR primer pair (see panel a for diagram).