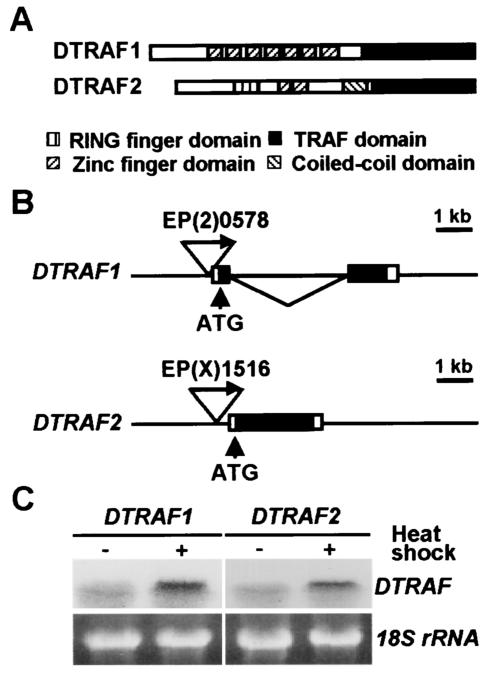
FIG. 1.
Characterization of DTRAF overexpression flies. (A) Schematic representation of the protein domains of DTRAF1 and DTRAF2. (B) EP fly lines for DTRAF genes. Two EP lines, EP(2)0578 and EP(X)1516, have a P-element in the 5′ flanking regions of DTRAF1 and DTRAF2, respectively. The triangle with an arrow represents the P-element, and ATG denotes the translational initiation site. Exons are indicated by boxes, and coding regions are highlighted by black boxes. (C) Inducible expression of DTRAFs in vivo. Using a GAL4/UAS system, ectopic expression of DTRAF1 or DTRAF2 was induced by heat shock at 37°C for 3 h, and their transcript levels were determined by Northern blot analysis. (Left panel) DTRAF1 mRNA from hs-GAL4/EP(2)0578; (right panel) DTRAF2 mRNA from EP(X)1516/X; hs-GAL4/+. 18S rRNA (18S rRNA) was used as a loading control.