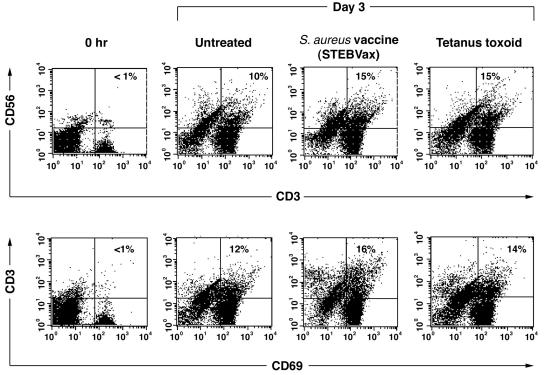
FIG. 5.
Increase in CD56+-T-cell frequency upon exposure to S. aureus vaccine (STEBvax) or tetanus toxoid. MNC from a tetanus toxoid- and S. aureus-immune donor were depleted of CD56+ cells and cultured (37°C, 5% CO2) with S. aureus vaccine (STEBVax) or tetanus toxoid (50 μg/ml). After 3 days of culture, cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. The dot plot representation shows the increase in the population of CD3+CD56+ and CD3+CD69+ T cells. The proportions of CD3+CD56+ cells were compared between the untreated group and the STEBVax and tetanus toxoid groups by chi-square test. Results showed that there was a significant difference in the proportion of positive cells between the STEBVax group and the untreated group [χ2(1) = 181.49; P < 0.0001]. Results also showed that there was a significant difference in the proportion of positive cells between the tetanus toxoid group and the untreated group [χ2(1) = 185.69; P < 0.0001]. The proportions of CD3+CD69+ cells were compared between the untreated group and the STEBVax and tetanus toxoid groups by chi-square test. Results also showed that there was a significant difference in the proportion of activated cells with recall antigens, i.e., between the STEBVax group and the untreated group [χ2(1) = 196.46; P < 0.0001] and between the tetanus toxoid group and the untreated group [χ2(1) = 69.43; P < 0.0001]. Results shown are from one representative experiment of three performed.