Figure 6. Role of CR3 in the uptake and intracellular survival of P. gingivalis: alveolar vs. peritoneal macrophages.
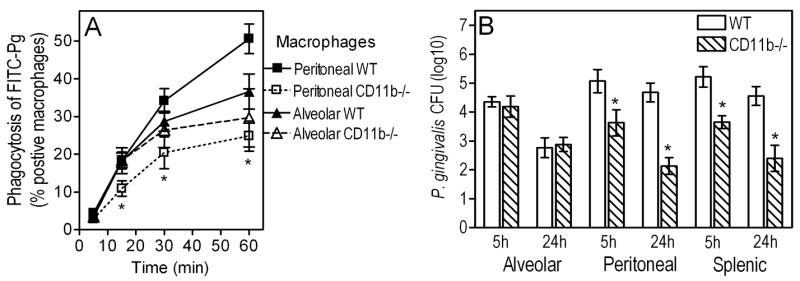
(A) Alveolar or peritoneal macrophages from wild-type (WT) or CR3-deficient (CD11b−/−) mice were incubated with P. gingivalis (MOI = 10:1) for the indicated times at 37°C. Uptake was assessed using FITC-labeled bacteria and flow cytometry after quenching extracellular fluorescence, and was expressed as percentage of FITC-positive macrophages. (B) The same macrophage groups, as well as wild-type and CD11b−/− splenic macrophages, were compared for their intracellular killing abilities against P. gingivalis (used at a MOI of 10:1) by means of an antibiotic protection-based survival assay. Results are presented as means ± SD (n = 3). In panel A, the asterisks show significantly (p < 0.05) reduced uptake by CD11b−/− AM compared to WT controls. In panel B, the asterisks show significantly (p < 0.05) reduced survival of P. gingivalis in the indicated CD11b−/− macrophages compared to WT controls.
