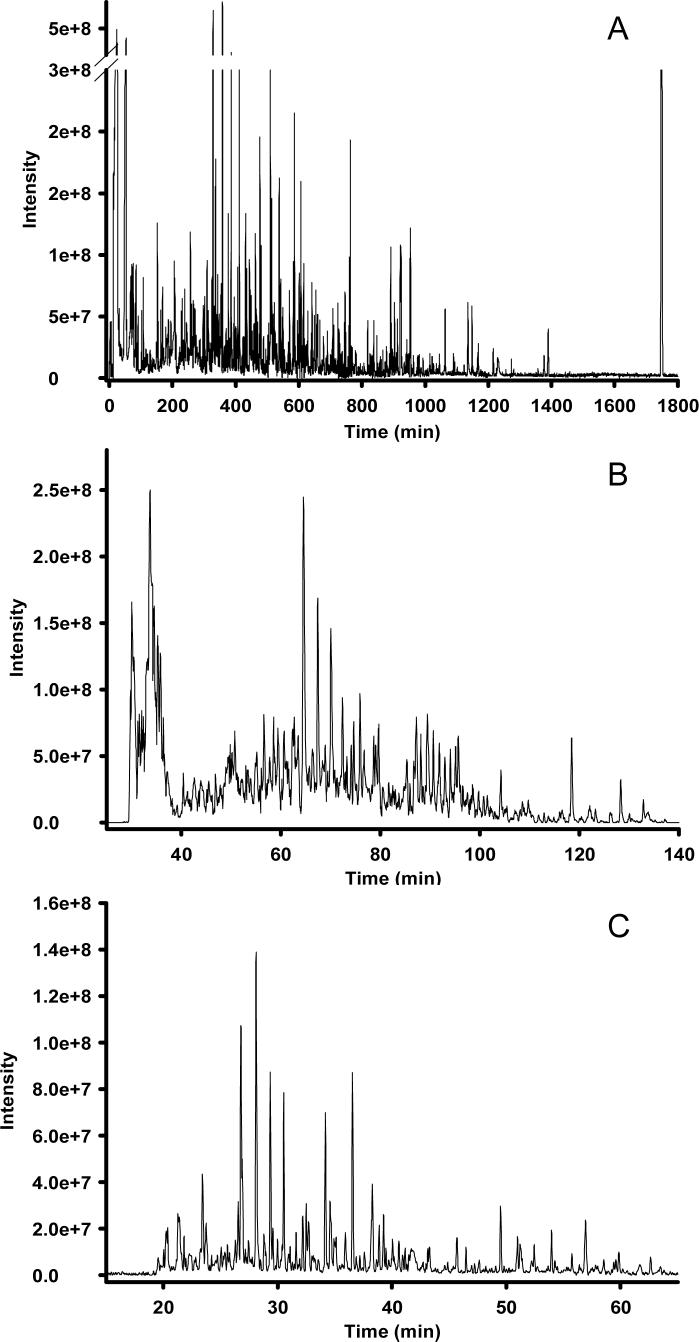
Figure 1. Analysis of the Shewanella oneidensis metabolome utilizing reversed-phase capillary LC coupled with FTICR MS.
High-resolution capillary LC separation of the S. oneidensis metabolome was performed using an 11 Tesla FTICR as the mass detector. The operating pressure of the LC was 20,000 psi and the reversed-phase C18 capillary columns are as follows: (A) 50 μm i.d. × 2 m, 3 μm dP, (B) 50 μm i.d. × 50 cm, 2 μm dP, (C) 50 μm i.d. × 20 cm, 1.4 μm dP. Peak-capacities of ∼1500, ∼500, and ∼350 were calculated for the separations shown in A, B, and C, respectively. Adapted from reference 28: Biomarkers Med., 1, T. Metz, Q. Zhang, J. Page, Y. Shen, S. Callister, J. Jacobs, and R. Smith, Future of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in metabolic profiling and metabolomic studies for biomarker discovery, 159−185, 2007, with permission from Future Medicine.