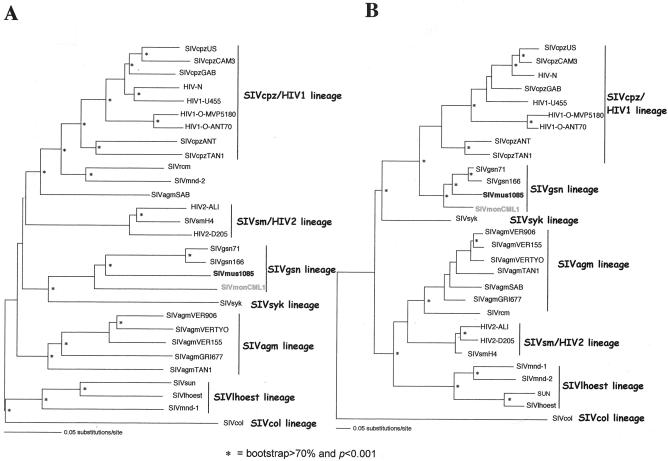
FIG. 6.
Unrooted maximum-likelihood trees of the pol (A) and env (B) genes, including 26 SIV-HIV strains of the six major SIV lineages, as well as other SIVs for which full-length sequences are available (SIVrcm, SIVmnd2, and SIVgsn) and the new SIVmon-99CMCML1 and SIVmus-01CM1085 isolates. The pol and env trees were inferred using only first and second codon positions, with the TrN + Inv + Γ (α = 1.3854; I = 0.1862) and the HKY + Inv + Γ (α = 1.1796; I = 0.2508; Ti/Tv = 0.9724) model of nucleotide substitution, respectively. Horizontal branch lengths are drawn to scale, with the bar representing 0.1 nucleotide replacements per site. The neighbor-joining method gives a similar tree topology. An asterisk along a branch indicates that the branch has a P value of <0.001 in the maximum-likelihood analysis and a percentage of bootstrap replicates (out of 1,000) of >70 in the neighbor-joining tree. α, shape parameter of the Γ distribution; I, proportion of invariable sites; Ti/Tv, expected transition/transversion ratio.