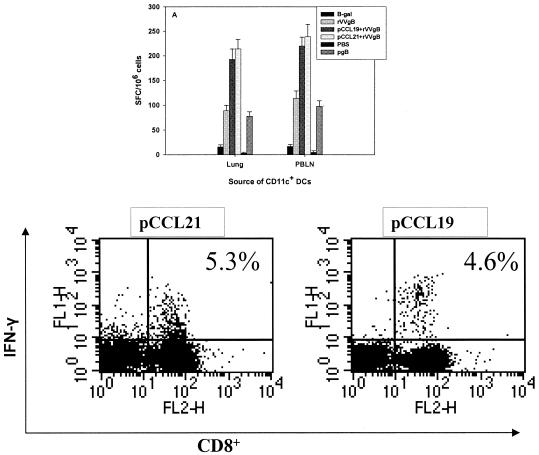
FIG. 2.
CD11c+ DCs isolated from lungs and PBLN of pCCR7L-treated mice are capable of activating CD8+ T cells from mice previously primed with HSV. Mice were treated with pCCR7L, β-Gal, or PBS i.n., and 3 days later pCCR7L-treated mice were immunized i.n. with rVVgB. One group was infected with rVVgB only. An IFN-γ ELISPOT assay was performed to quantitate the functional capability of CD11c+ DCs originating from lungs and PBLN of pCCR7L-treated and control mice. Seven days following immunization lungs and PBLN were removed and CD11c+ DCs were prepared, purified by MACS, and incubated with splenocytes from mice primed earlier with HSV. CD11c+ DCs (2 × 104) were added to 105 splenocytes per well. (A) Spot-forming cells after stimulation with lung or PBLN CD11c+ DCs; (B) IFN-γ secretion by CD8+ T cells isolated from lungs of pCCR7L-treated mice upon restimulation in vitro with HSV-gB498-505. Intracellular staining for IFN-γ was performed as described in Materials and Methods.