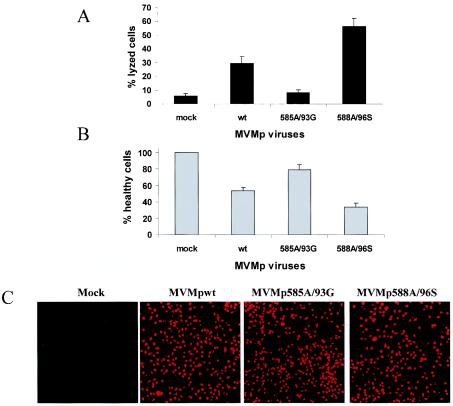
FIG. 6.
Varying cytotoxicity of wild-type and mutant MVMp viruses. The indicated virus stocks were tested for their ability to jeopardize the survival of A9 fibroblasts after infection at a multiplicity of 10 CFU/cell and further incubation for 3 days. (A) The virus lytic activity was measured through quantification of the cytoplasmic LDH released into the medium, expressed as a percentage of total LDH (determined after lysis of the whole culture with detergent). (B) The cell-killing activity of the different viruses was assessed by determining the reduction in the number of living cells (still able to reduce MTT) in the infected population, a value expressed as the percentage of the value for mock-treated cultures. The same cultures were used for panels A and B. The data shown are means with standard deviation bars from 10 independent experiments carried out each in triplicate. (C) NS1 produced by wild-type and mutant MVMp viruses was detected by indirect immunofluorescence in parallel cultures. Images were obtained by using a ×16 magnification lens.