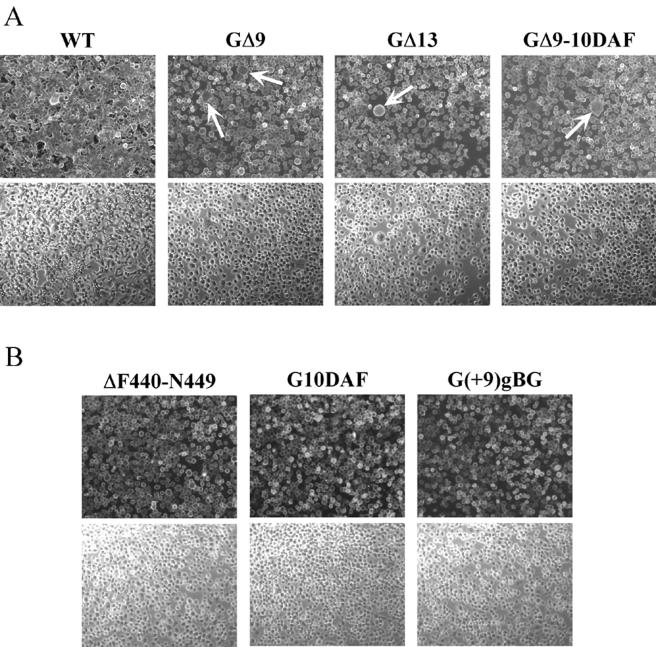
FIG. 5.
Syncytium formation assays. Approximately 5 × 105 BHK-21 cells were infected at a multiplicity of infection of 10 for 1 h at 37°C. At 6 h postinfection, the cells were treated with fusion medium buffered to pH 5.9, 5.5, or 5.2 for 1 min at room temperature. The medium was replaced with DMEM-5% FBS, and the cultures were incubated at 37°C for 20 min to 1 h. Cells were then fixed and processed for indirect immunofluorescence using a G-specific MAb (I1). Rhodamine-conjugated goat anti-mouse antibody was used as the secondary antibody. Fluorescence and phase-contrast images were digitally captured using a Zeiss Axiocam fitted on a Zeiss Axiophot microscope with a 10× water-immersible ceramic objective. The images were then processed using Adobe Photoshop to adjust for brightness and contrast. (A) Syncytium formation induced in cells infected with rVSV-WT, -GΔ9, -GΔ13, and -GΔ9-10DAF strains after treatment with fusion medium buffered to pH 5.9. The arrows point to small syncytia in the mutant-infected cells. (B) Cells infected with rVSV-ΔF440-N449, -G10DAF, and -G(+9)gBG after treatment at pH 5.2. Upper and lower panels correspond to fluorescence and phase-contrast images, respectively.