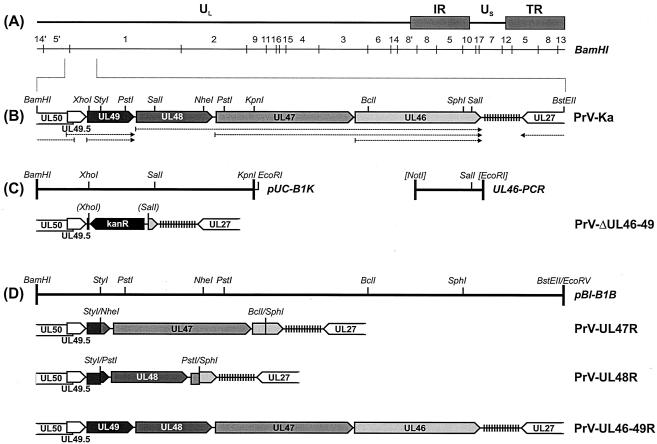
FIG. 1.
Generation of virus mutants. (A) Schematic map of the PrV genome, which consists of a UL region and a US region which is bracketed by inverted repeat sequences (IR and TR). The positions of BamHI restriction fragments are indicated. (B) Enlarged map of the investigated part of the genome of wild-type PrV-Ka with relevant restriction sites. The positions of repetitive sequences (vertical lines) and the transcriptional organization (dotted arrows) of the UL50 to UL27 genes (pointed rectangles) are also shown. (C) A cloned BamHI-KpnI fragment of the PrV-Ka genome (pUC-B1K) and a PCR product containing artificial restriction sites (UL46-PCR) were utilized for construction of the deletion mutant PrV-ΔUL46-49 in which the UL46 to UL49 genes were replaced by a kanamycin resistance gene (kanR). Restriction sites in parentheses were lost during cloning. (D) Plasmid pBl-B1B contains a BamHI-BstEII fragment of the PrV-Ka genome and was used for generation of a PrV-ΔUL46-49 rescue mutant (PrV-UL46-49R). The transfer plasmids for generation of the single-gene revertants PrV-UL47R and PrV-UL48R were derived from pBl-B1B by subcloning (see text).