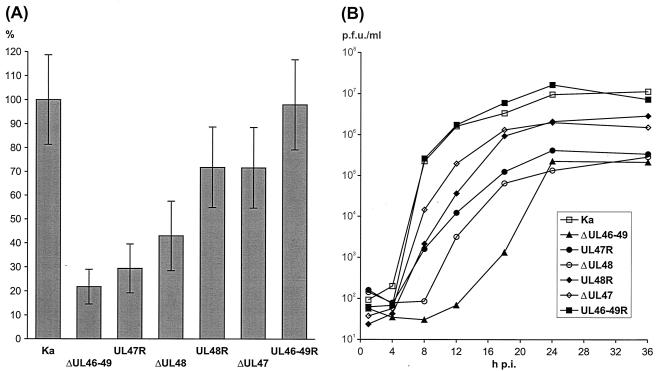
FIG. 3.
Growth properties in RK13 cells of PrV-Ka; deletion mutants PrV-ΔUL46-49, PrV-ΔUL47, and PrV-ΔUL48; and revertants PrV-UL47R, PrV-UL48R, and PrV-UL46-49R. (A) After incubation under medium containing 6 g of methylcellulose/liter for 48 h, the infected cell monolayers were fixed with ethanol, and virus plaques were visualized by immunofluorescence reactions of a gC-specific MAb and fluorescein-conjugated secondary antibodies (Dako). The mean diameters of 30 single plaques per virus mutant were determined, and percentages of the wild-type (PrV-Ka) size were calculated. Error bars, standard deviations. (B) For analysis of one-step growth kinetics cells were infected at a MOI of 2 and incubated on ice for 1 h. Then, prewarmed medium was added, and incubation was continued at 37°C. After 1 h, nonpenetrated virus was inactivated by low-pH treatment. Immediately thereafter, as well as 4, 8, 12, 16, 24, 36, and 48 h after the temperature shift, cells were scraped into the medium and lysed by freezing and thawing. Progeny virus titers were determined by plaque assays, and the average results of two independent experiments are shown. p.i., postinfection.