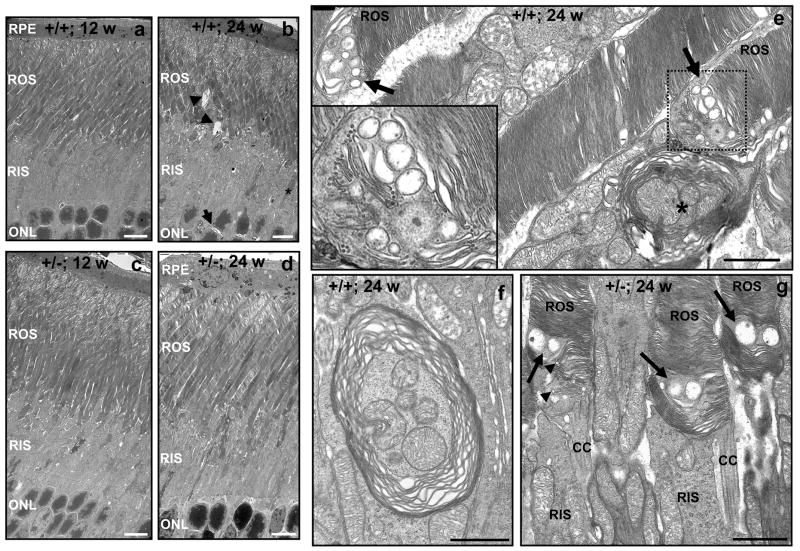
Figure 2.
Electron micrographs depicting the age-dependent ultrastructural changes of inner and outer segments of photoreceptors of 12- and 24-week old RanBP2+/+ and RanBP2+/− mice upon prolonged light exposure. There is an overall increase in the subcellular disorganization of morphological features of the inner and outer segments of photoreceptors in 24-week old RanBP2+/+ mice (b) compared to 12-week old RanBP2+/− mice (a). This is reflected by an increase of cystoid spaces between nuclei (arrow) and outer segments (arrowheads), shrinking and condensed inner segments (star), formation of vacuoles in the inner segment, and dilation of the disks at the tip of the outer segments. The development of these subcellular pathologies, except for the dilation of the disks, was strongly decreased in 24-week old RanBP2+/− mice (d) compared to 12-week old RanBP2+/− mice (c). e, f, and g, depict high magnification images of single membrane multivesicular bodies at the base of the outer segments (e), large vesicular body duets (arrows) and crescent vesicles in nascent disk rims (arrowheads) at the base of the outer segments of RanBP2+/− mice (f), and multilamellar bodies engulfing mitochondria in RanBP2+/+ mice (e, star; g). Legend: RPE, retina pigment epithelium; ROS, rod outer segment of photoreceptors; RIS, rod inner segment of photoreceptors; ONL, outer nuclear layer (nuclei of photoreceptors); CC, connecting cilium. Scale bar in a-d, 6 μm; scale bar in e-g, 1 μm.