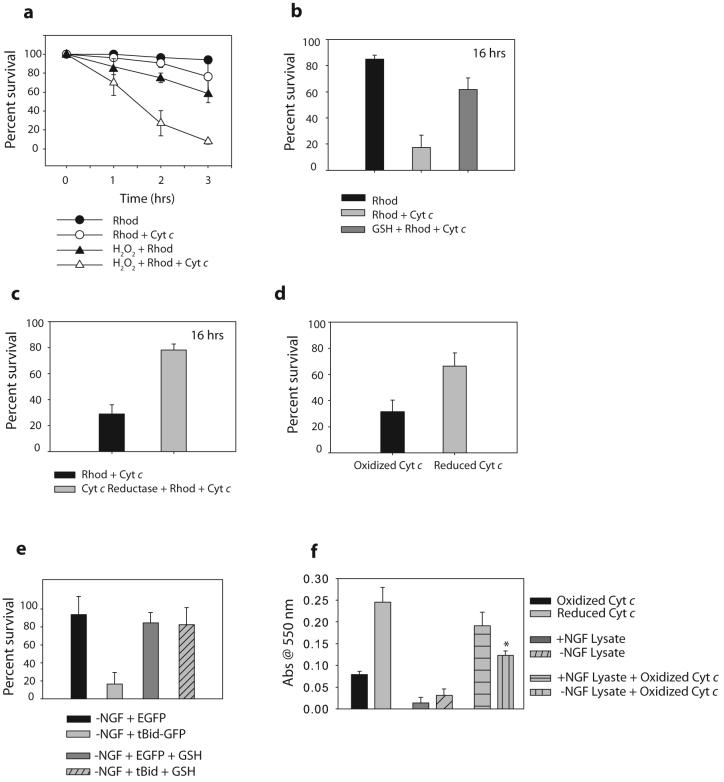
Figure 2. Oxidation of cytochrome c increases its apoptotic activity.
a) XIAP -/- sympathetic neurons were treated with 20-50 μM of H2O2 for 20 minutes, followed by injection with cytochrome c protein and rhodamine, or rhodamine dye alone. Cell survival was assessed at various time points following injection. b) XIAP -/- sympathetic neurons were treated with 10 mM GSH ethyl ester for 12 hrs, followed by injection of cytochrome c along with rhodamine, or rhodamine alone. Cell survival was assessed at 16 hrs following injection. c) XIAP -/- sympathetic neurons were injected with either cytochrome c, or cytochrome c that was pre-incubated with 10 Units/ml of cytochrome c reductase. Cell survival was assessed at 16 hrs following injection. d) XIAP -/- sympathetic neurons were injected with either cytochrome c, or cytochrome c that had been pre-incubated with DTT (and subsequently separated) to reduce this cytochrome c. Percent survival was assessed after 6 hrs. e) XIAP -/- sympathetic neurons were deprived on NGF for 8 hrs in the presence of 10 mM GSH, followed by injection with EGFP or tBid-GFP constructs. Cell survival was quantified by cell morphology and expressed as a percentage of alive and healthy green cells at 16 hrs compared to 5 hrs post-injection. f) Exogenous cytochrome c (which is primarily oxidized) was added at a concentration of 10 uM to neuronal extracts, and Abs550 was measured following a 15 min. incubation. Control experiments measuring Abs550 of reduced or oxidized cytochrome c are also shown. Results are mean (±SEM) of three independent experiments.