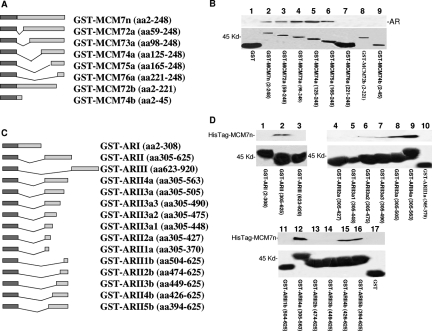
Figure 2.
Identification of sequence motifs required for AR and MCM7 interaction. A: Schematic diagram of GST-MCM7n and its deletion mutants. B: Binding of AR with GST-MCM7n deletion mutants. The GST-MCM7n fusion protein or its mutants were purified from glutathione columns, and binding assays with AR were performed with protein extracts from LNCaP cells. After extensive washes, the bindings were visualized with SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies against AR. Top: Immunoblot with anti-AR antibodies. Bottom: Coomassie staining of glutathione column-purified GST-MCM7n fusion proteins. The names of fusion proteins and MCM7 coding sequences are indicated. C: Schematic diagram of GST-AR fusion proteins. D:In vitro binding assays of bacterial expressed HisTag-MCM7n and GST-AR fusion proteins. The HisTag-MCM7n protein was purified through a histidine tag column. The purified HisTag-MCM7n protein was applied to GST-AR fusion protein to perform binding assays as described in B. The bindings of GST-ARs and HisTag-MCM7n were visualized through immunoblots with antibodies against MCM7. Top: Immunoblot with anti-MCM7 antibody. Bottom: Coomassie staining of glutathione column-purified GST-AR fusion proteins. Names of fusion proteins and AR coding sequences are indicated. These binding assays have been repeated seven times. Similar results were obtained.