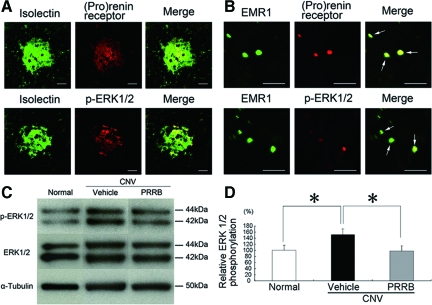
Figure 4.
(Pro)renin receptor and phosphorylated ERK1/2 are present in CNV-associated macrophages and vascular endothelial cells, and PRRB inhibits ERK1/2 activation following CNV induction. The immunohistochemical analyses show (pro)renin receptor and phosphorylated ERK1/2 in isolectin B4-positive endothelial cells (A) and EMR1-positive macrophages (B). A: Green fluorescence from isolectin B4 (left) and red fluorescence from an anti-(pro)renin receptor (middle, top) or an anti-phosphorylated ERK1/2 antibody (middle, bottom) identified the isolectin B4-positive endothelial cells as having (pro)renin receptor or phosphorylated ERK1/2, respectively, when the images were superimposed (right). Scale bars = 50 μm. B: Green fluorescence from an anti-EMR1 antibody (left) and red fluorescence from an anti-(pro)renin receptor (middle, top) or an anti-phosphorylated ERK1/2 antibody (middle, bottom) identified the EMR1-positive macrophages as having (pro)renin receptor or phosphorylated ERK1/2, respectively, when the images were superimposed (arrows, right). Scale bars = 50 μm. C-D: Western blotting for phosphorylated and total levels of ERK1/2 in the RPE-choroid after photocoagulation. Relative phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in the RPE-choroid complex, increased by inducing CNV, was suppressed by PRRB treatment (n = 11 to 13. *P < 0.05).