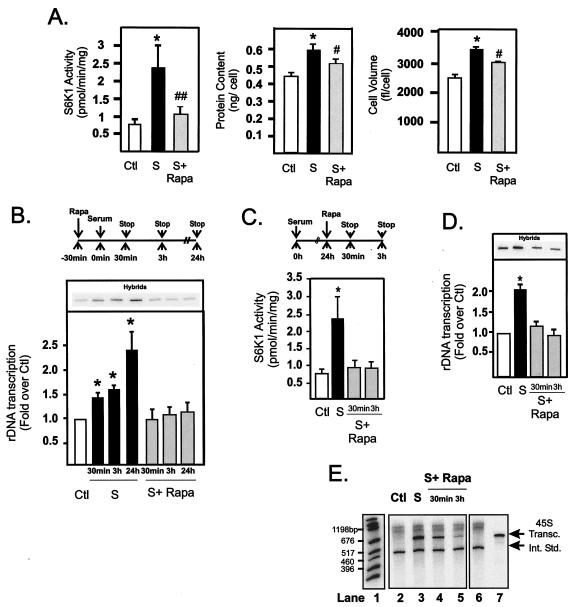
FIG. 1.
Regulation of NIH 3T3 cell growth correlates with rapid and sustained activation of rDNA transcription by mTOR. NIH 3T3 cells were plated in DMEM with 10% FBS, allowed to grow overnight, and made quiescent by incubation for 24 h in DMEM with 0.5% BSA (serum starved as a control). After serum starvation, cells were pretreated with rapamycin (20 nM) or vehicle (ethanol) for 30 min before stimulation with DMEM plus 10% FBS for 30 min, 3 h, or 24 h. Cells harvested at 24 h were assayed for S6K1 activity, protein content per cell, and cell volume (A) as described in Materials and Methods. Cells harvested at 30 min, 3 h, and 24 h were assayed for endogenous rDNA transcription rates by nuclear run-on analysis (B) as described in Materials and Methods. Alternatively, quiescent cells were stimulated with 10% FBS for 24 h before treatment with rapamycin (20 nM) for 30 min and 3 h as illustrated in the schematic (C), then harvested and assayed for S6K1 activity (C), endogenous rDNA transcription (D), and for their ability to transcribe 0.1 μg of 45S template gene in vitro (E) as described in Materials and Methods. Lane 1, markers; lanes 2 to 5, 45S transcripts (45S Transc.); lane 6, internal standard (Int. Std.); lane 7, 45S transcript. Values that are significantly different (P < 0.05) from the control values (*) and values that are significantly different (P < 0.05 [#] and P < 0.005 [##]) from the values for serum-treated cells (n = 4 to 7) are indicated. Abbreviations: Ctl, control; S, 10% FBS; S+ Rapa, 10% FBS plus 20 nM rapamycin.